These NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.3 Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Exercise 7.3
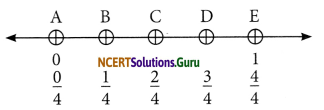
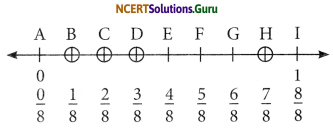
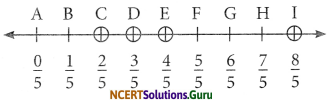
Question 1.
Write the fractions. Are all these fractions equivalent?
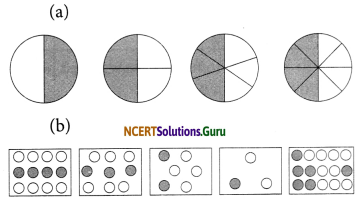
Answer:
(a) We can find fraction in each figure by the formula
\(\frac{\text { Dark part }}{\text { Total part }}\)
\(=\frac{1}{2}, \frac{2}{4}=\frac{1}{2}, \frac{3}{6}=\frac{1}{2}, \frac{4}{8}=\frac{1}{2}\)
These all fractions are equivalent.
(b) We can find fraction in each figure by the formula Dark part Total part
\(\frac{\text { Dark part }}{\text { Total part }}\)
\(=\frac{4}{12}=\frac{1}{3}, \frac{3}{9}=\frac{1}{3}, \frac{2}{6}=\frac{1}{3}, \frac{6}{15}=\frac{2}{5}\)
These all are not equivalent fractions.

Question 2.
Write the fractions and pair up the equivalent fractions from each row.
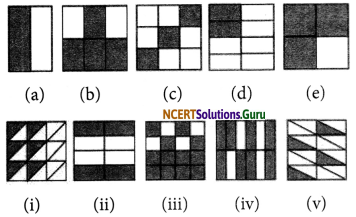
Answer:
Equivalent fraction would be then
(a) and (ii) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(b) and (iv) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(c) and (i) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(d) and(v)= \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(e) and (iii) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
Question 3.
Replace □ in each of the following by the correct number:
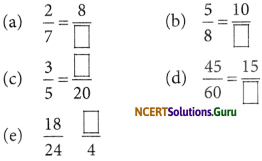
Answer:
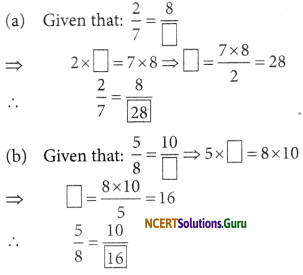
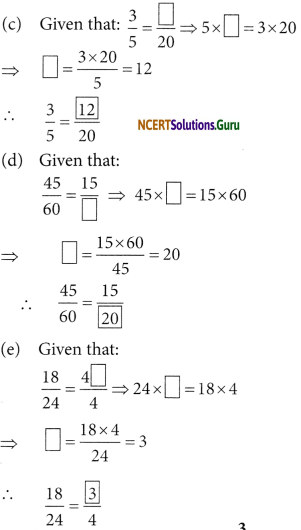

Question 4.
Find the equivalent fraction of \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 }\) having
(a) denominator 20 1
(b) numerator 9
(c) denominator 30
(d) numerator 27
Answer:
To find an equivalent fraction, we may multiply/divide both the numerator and the denominator by the same number.
| (a) |
To make denominator 20, we need to multiple both by 4 |
\(\frac { 12 }{ 20 }\) |
| (b) |
To make numerator 9, we need to multiple both by 3 |
\(\frac { 9 }{ 15 }\) |
| (c) |
To make denominator 30, we need to multiple both by 6 |
\(\frac { 18 }{ 30 }\) |
| (d) |
To make numerator 27, we need to multiple both by 9 |
\(\frac { 27 }{ 45 }\) |
Question 5.
Find the equivalent fraction of \(\frac { 36 }{ 48 }\) with
(a) numerator 9
(b) denominator 4
Answer:
| (a) |
To make numerator 9, we need to divide both by 4 |
\(\frac { 9 }{ 12 }\) |
| (b) |
To make denominator 4, we need to divide both by 12 |
\(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) |
(a) Hence, the equivalent fraction is \(\frac { 9 }{ 12 }\)
(b) Hence, the equivalent fraction is \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\)
Question 6.
Check whether the given fractions are equivalent:
(a) \(\frac{5}{9}, \frac{30}{54}\)
(b) \(\frac{3}{10}, \frac{12}{50}\)
(c) \(\frac{7}{13}, \frac{5}{11}\)
Answer:
(a) \(\frac{5}{9}, \frac{30}{54}\)
We have 5 x 54 = 270
and 9 x 30 = 270
Here 5 x 54 = 9 x 30
\(\frac{5}{9}\) and \(\frac{30}{54}\) are equivalent fractions.
(b) \(\frac{3}{10}, \frac{12}{50}\)
We have 3 x 50 = 150
and 10 x 12 = 120
Here 3 x 50 ≠ 10 x 12
\(\frac{3}{10}\) and \(\frac{12}{50}\) are not equivalent fractions.
(c) \(\frac{7}{13}, \frac{5}{11}\)
We have 7 x 11 = 77 and 5 x 13 = 65
Here 7 x 11 ≠ 5 x 13
\(\frac{7}{13}\) anCl \(\frac{5}{11}\) ecluivalent fractions.

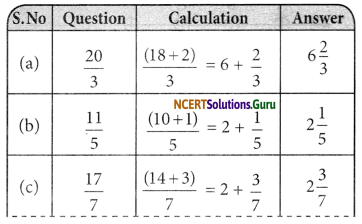
Question 7.
Reduce the following fractions to simplest form:
(a) \(\frac { 48 }{ 60 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 150 }{ 60 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 84 }{ 98 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 12 }{ 52 }\)
(e) \(\frac { 7 }{ 28 }\)
Answer:
To reduce the fraction to simplest form, we need to find the HCF of numerator and denominator
| (a) |
HCF of 48 and 60 is 12, So dividing by 12 on both numerator and denominator |
\(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) |
| (b) |
HCF of 150 and 60 is 12, So dividing by 30 on both numerator and denominator |
\(\frac { 5 }{ 2 }\) |
| (c) |
HCF of 84 and 98 is 14, So dividing by 14 on both numerator and denominator |
\(\frac { 6 }{ 7 }\) |
| (d) |
HCF of 12 and 52 is 4, So dividing by 4 on both numerator and denominator |
\(\frac { 3 }{ 13 }\) |
| (e) |
HCF of 7 and 28 is 7, So dividing by 7 on both numerator and denominator |
\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) |
Question 8.
Ramesh had 20 pencils, Sheelu had 50 pencils and Jamaal had 80 pencils. After 4 months, Ramesh used up 10 pencils, Sheelu used up 25 pencils and Jamaal used up 40 pencils. What fraction did each use up? Check if each has used up an equal fraction of her/his pencils?
Answer:
Fraction of pencils used by Ramesh
\(=\frac{\text { Used pencil }}{\text { Total pencil }}=\frac{10}{20}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Fraction of pencils used by Sheelu
\(=\frac{\text { Used pencil }}{\text { Total pencil }}=\frac{25}{50}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Fractions of pencils used by Jamaal
\(=\frac{\text { Used pencil }}{\text { Total pencil }}=\frac{40}{80}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Yes, they have all used up an equal fraction of his/her pencils i.e. \(\frac{1}{2}\)

Question 9.
Match the equivalent fractions and write two more for each.
| (i) |
\(\frac { 250 }{ 440 }\) |
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) |
| (ii) |
\(\frac { 180 }{ 200 }\) |
(b) \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) |
| (iii) |
\(\frac { 660 }{ 990 }\) |
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) |
| (iv) |
\(\frac { 180 }{ 360 }\) |
(d) \(\frac { 5 }{ 8 }\) |
| (v) |
\(\frac { 220 }{ 550 }\) |
(e) \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\) |
Answer:
| (i) |
\(\frac { 250 }{ 440 }\)(Dividing both numerator and denominator by 50) |
(d) \(\frac { 5 }{ 8 }\) |
| (ii) |
\(\frac { 180 }{ 200 }\) (Dividing both numerator and denominator by 20) |
(e) \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\) |
| (iii) |
\(\frac { 660 }{ 990 }\) (Dividing both numerator and denominator by 330) |
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) |
| (iv) |
\(\frac { 180 }{ 360 }\) (Dividing both numerator and denominator by 180) |
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) |
| (v) |
\(\frac { 220 }{ 550 }\) (Dividing both numerator and denominator by 110) |
(b) \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) |
![]()
![]()