Do you need some help in preparing for your upcoming Class 11 Chemistry exams? We’ve compiled a list of MCQ on Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers to get you started with the subject. You can download NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques with Answers Pdf free download, and learn how smart students prepare well ahead with MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry with Answers.
Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1.
Which among the following statement is not true?
(a) In liquid, particles are less regularly arranged and are free to move
(b) Boiling involves breaking up of group of molecules in liquid
(c) Boiling involves separation of oppositely charged ions
(d) Thermal energy of particles overcome cohesive forces that hold them
Answer
Answer: (c) Boiling involves separation of oppositely charged ions
Explanation:
Boiling involves separation of oppositely charged ions and makes them as individual ions.
Question 2.
Identify the chiral molecule among the following:
(a) Isopropyl alcohol
(b) 2-pentanol
(c) 1-bromo 3-butene
(d) Isobutyl alcohol
Answer
Answer: (d) Isobutyl alcohol
Explanation:
Chirality is the condition for a molecule to be optically active and here isobutyl alcohol is the only compound is optically active and hence it is the chiral molecule.
Question 3.
Which element is estimated by Carius method
(a) Carbon
(b) Hydrogen
(c) Halogen
(d) Nitrogen
Answer
Answer: (c) Halogen
Explanation:
Halogen element is estimated by Carius method
Question 4.
A solution of(+) – 2 – chloro – 2 – phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of small amounts of SbCl5 due to the formation of
(a) Carbanion
(b) Carbene
(c) Free radical
(d) Carbocation
Answer
Answer: (d) Carbocation
Explanation:
SbCl5 pulls Cl– to form SbCl–6 leaving behind planar C6H5−C+H−CH3 carbonium ion. It can be attacked from either side leading to racemic mixture.
Question 5.
Which of the following acids has the smallest dissociation constant?
(a) CH3CHFCOOH
(b) FCH2CH2COOH
(c) BrCH2CH2COOH
(d) CH3CHBrCOOH
Answer
Answer: (c) BrCH2CH2COOH
Explanation:
BrCH2CH2COOH is least acidic or has less Ka i.e., dissociation constant. It is A due to lesser -I effect of Br than F and B Br atom further away form −COOH group.
Question 6.
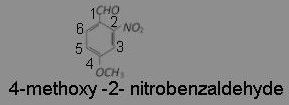
What is the correct IUPAC name of
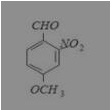
(a) 4-methoxy-2-nitrobenzaldehyde
(b) 4-formyl-3-nitro anisole
(c) 4-methoxy-6-nitrobenzaldehyde
(d) 2-formyl-5-methoxy nitrobenzene
Answer
Answer: (a) 4-methoxy-2-nitrobenzaldehyde
Explanation:
IUPAC name is 4-methoxy-2-nitrobenzaldehyde
Question 7.
0.5 g of hydrocarbon gave 0.9 g water on combustion. The percentage of carbon in hydrocarbon is
(a) 75.8
(b) 80.0
(c) 56.6
(d) 28.6
Answer
Answer: (b) 80.0
Explanation:
Percentage% of H =(2/18) × [(weight of H2O)/(weight of organic compound)] × 100
=(2/18) × [(0.9)/(0.5)] × 100 = 20
Since percentage of hydrogen is 20. Therefore, remaining is carbon i.e. 80 %.
Question 8.
0.92 g of an organic compound was analysed by combustion method. The mass of the U- tube increased by 1.08 g. What is the percentage of hydrogen in the compound?
(a) 13.04%
(b) 52.17%
(c) 65.21%
(d) 11.30%
Answer
Answer: (a) 13.04%
Explanation:
For Percentage % of H,
(Percentage % of H)/(H2O) = (2/18) × [(weight x H2O)/Weight of organic compound)] × 100
= (2/18) × (1.08/0.92) × 100
= 13.04 %
Question 9.
What is the state of hybridisation of carbon in carbanion?
(a) sp
(b) sp²
(c) sp³
(d) sp²d.
Answer
Answer: (c) sp³
Explanation:
In carbanion the carbon atom is sp³ hybridised and the geometry is pyramidal.
Question 10.
An organic compound contains C = 38.8 H = 16 and N = 45.2. Empirical formula of the compound is
(a) CH3NH2
(b) CH3CN
(c) C2H5CN
(d) CH2(NH)2
Answer
Answer: (a) CH3NH2
Question 11.
59 g of an amide obtained from a carboxylic acid, RCOOH, liberated 17 g of ammonia upon heating with alkali. The acid is
(a) Formic Acid
(b) Acetic Acid
(c) Propionic Acid
(d) Benzoic Acid
Answer
Answer: (b) Acetic Acid
Question 12.
The displacement of electrons in a multiple bond in the presence of attacking reagent is called
(a) Inductive effect
(b) Electromeric effect
(c) Resonance
(d) Hyper conjugation
Answer
Answer: (b) Electromeric effect
Explanation:
The electromeric effect is a temporary effect brought into play at the requirement of attacking reagent. Electromeric effect refers to a molecular polarizability effect occurring by an intra-molecular electron displacement. It is the temporary effect.
Question 13.
The molecular formula C5H12 contains how many isomeric alkanes?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (c) 3
Explanation:
n-pentane, 2-ethylpropane, and 2-methylbutane are the 3 isomeric alkanes of C5H1 (pentane).
Question 14.
If two compounds have the same empirical formula but different molecular formula they must have
(a) Different percentage composition
(b) Different molecular weight
(c) Same viscosity
(d) Same vapour density
Answer
Answer: (b) Different molecular weight
Explanation:
If molecular formula is different than molecular weight is also different.
Question 15.
Inductive effect involves
(a) displacement of σ electrons
(b) delocalization of π electrons
(c) delocalization of σ-electrons
(d) displacement of π-electrons
Answer
Answer: (a) displacement of σ electrons
Explanation:
During inductive effect shifting of a electrons takes place due to which partially charges are developed on the atom.
+δ” + δ′ + δ −δ
C− C− C −C1−
Question 16.
A gas mixture contains 50% helium and 50% methane by volume. What is the percent by weight of methane in the mixture
(a) 75%
(b) 50%
(c) 80.03%
(d) 19.97%
Answer
Answer: (c) 80.03%
Explanation:
Given the Solution contains He + CH4
Their molecular weight = 4 + 16 = 20 % wt of CH4
= (weight of CH4)/(Total wt × 100)
= (16/20) × 100
= 80.0
Question 17.
Which of the following physical properties differ for each of a pair of enantiomers?
(a) solubility in ethanol
(b) direction of rotation of plane-polarized light
(c) boiling point and melting point
(d) index of refraction
Answer
Answer: (b) direction of rotation of plane-polarized light
Explanation:
Enantiomers are equal in all their physical properties except for their optical rotation, as they rotate the plane of polarized light by equal amounts in opposite directions.
Question 18.
The reaction of HCOOH with conc.H2SO4 gives which of the following compound?
(a) CO2
(b) CO
(c) Oxalic Acid
(d) Acetic acid
Answer
Answer: (b) CO
Question 19.
What is the state of hybridisation of carbon in carbanion?
(a) sp
(b) sp²
(c) sp³
(d) sp²d.
Answer
Answer: (c) sp³
Explanation:
In carbanion the carbon atom is sp³ hybridised and the geometry is pyramidal.
Question 20.
Which among the following is formed when an alcohol is dehydrated?
(a) alkane
(b) alkyne
(c) alkene
(d) aldehyde
Answer
Answer: (c) alkene
Explanation:
In elimination reaction, when protic acids react with alcohol, they lose water molecule to form alkenes.
We hope you found this CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers helpful. If you have any questions about NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques with Answers Pdf free download, please share them in the comment box below and we will get back to you at the earliest possible time.