Do you need some help in preparing for your upcoming Class 12 Accountancy exam? We’ve compiled a list of MCQ questions on Cash Flow Statement Class 12 MCQs Questions with Answers to get you started with the subject. You can download NCERT MCQ Questions for Chapter 11 Cash Flow Statement with Answers Pdf free download, and learn how smart students prepare well ahead MCQ Questions for Class 12 Accountancy with Answers.
Cash Flow Statement Class 12 MCQs Questions with Answers
Who doesn’t want a head start on their exams? Get the latest study material for MCQ Questions for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 11 Cash Flow Statement with Answers to help you prepare!
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs):
Question 1.
While preparing Cash Flow Statement, match the following activities: (CBSE SP 2019-20)
I. Payment of cash to acquire Debenture by (a). Financing activity an Investing Company
II. Purchase of Goodwill (b). Investing Activity
III. Dividend paid by manufacturing company (c). Operating activity
Answer
Answer: I – c, II – b, III – a.
Question 2.
Which of the following is the source of cash?
(a) Cash deposited into bank
(b) Cash withdrawn from the bank
(c) Sale of marketable securities
(d) Sale of goods for cash costing ₹ 20,000 for ₹ 16,000.
Answer
Answer: (d) Sale of goods for cash costing ₹ 20,000 for ₹ 16,000.
Question 3.
While calculating cash flows from operating profit, which of the following is not considered in the net profit?
(а) Amortisation of goodwill
(b) Writing off bad debts
(c) Writing off depreciation
(d) Interest paid on bank overdraft
Answer
Answer: (b) Writing off bad debts
Question 4.
Which of the following statement is incorrect about cash flow statement?
(a) It provides information about cash inflows and cash outflows .
(b) It provides information of flows of cash under three major categories
(c) It reconciles bank balance with the bank balance as per bank statement
(d) It helps in preparing cash budget
Answer
Answer: (c) It reconciles bank balance with the bank balance as per bank statement
Question 5.
Which of the following will come under operating activity?
(a) Issue of shares for cash
(b) Interest received on short-term investments
(c) Trading commission received by a manufacturing company
(d) Sale of marketable securities
Answer
Answer: (c) Trading commission received by a manufacturing company
Question 6.
Which of the following will not come under anywhere in cash flow statement?
(a) Repayment of borrowings
(b) Issue of bonus shares
(c) Sale of investments
(d) Dividend paid
Answer
Answer: (b) Issue of bonus shares
Question 7.
A plant whose original cost was ₹ 40,000, accumulated depreciation provided till the date of sale was ₹ 15,000 was sold at 20% above the book value. Cash flow from operating activities will be
(a) ₹ 48,000
(b) ₹ 30,000
(c) ₹ 18,000
(d) ₹ 25,000
Answer
Answer: (b) ₹ 30,000
Question 8.
Where will you show sale and purchase of shares and securities if it relates to revenue generating activity?
(a) Cash flow from investment activities
(b) Cash flows from financing activities
(c) Cash flows from operating activities
(d) Cash and cash equivalents
Answer
Answer: (c) Cash flows from operating activities
Question 9.
Which of the following transaction is always shown under financing activities?
(a) Interest received on investments
(b) Interest paid on investments
(c) Dividend paid
(d) Dividend received
Answer
Answer: (c) Dividend paid
Question 10.
Investments made by a financial enterprise with the purpose to resell after the expiry of three months will come under which of the following activity?
(a) Investment
(b) Financing
(c) Operating
(d) Cash equivalents
Answer
Answer: (c) Operating
Question 11.
Investments made with the purpose to resell after the expiry of three months will come under which of the following activity?
(a) Investment
(b) Financing
(c) Operating
(d) Cash equivalents
Answer
Answer: (d) Cash equivalents
Question 12.
Kaveri Ltd. A financing company obtained loans and advances of ₹ 5.00,000 during the year @ 12% p.a. it will be included in which of the following activities while preparing the cash flow statement? (CBSE Compartment Delhi 2015)
(a) Investing Activities
(b) Financing Activities
(c) Both Investing and Financing Activities
(d) Operating Activities
Answer
Answer: (d) Operating Activities
Question 13.
Cash deposit with the bank with a maturity date after two months belongs to which of the following while preparing cash flow statement: (CBSE Sample Paper 2015)
(a) Investing Activities
(b) Financing Activities
(c) Cash and Cash Equivalents
(d) Operating Activities
Answer
Answer: (c) Cash and Cash Equivalents
Question 14.
Which of the following transactions will not result into flow of cash? (CBSE Delhi 2014)
(a) Issue of equity shares of ₹ 1,00,000.
(b) Purchase of machinery of ₹ 1,75,000
(c) Redemption of 9% debentures ₹ 3,50,000
(d) Cash deposited into bank ₹ 15,000
Answer
Answer: (d) Cash deposited into bank ₹ 15,000
State whether the following statements are true or false:
Question 15.
‘Patents purchased by a company will be an operating activity.
Answer
Answer: False
Question 16.
Cash Flow Statement helps in reconciling closing bank balance with the balance as per bank statement.
Answer
Answer: False
Question 17.
Receipt of dividend on investment is always inflow of cash under investing activities for all types of companies.
Answer
Answer: False
Question 18.
Cash flow statement is different from cash book.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 19.
Tax on capital gains due to sale of non-current assets are shown under investing activities.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 20.
Increase or decrease in bank overdraft and cash credit is shown under financing activities.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 21.
Rent received form immovable property held as investments is shown under operating activities
Answer
Answer: False
Question 22.
Loans and advances granted is an operating activity for a financial enterprise.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 23.
Sale and purchase of marketable securities do not involve any flow of cash.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 24.
Amortisation of intangible asset is a non-cash and non-operating item.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 25.
Rental Income on the property held as stock is shown under operating activities for a non manufacturing enterprise.
Answer
Answer: True
Fill in the blanks with correct word:
Question 26.
Marketable Securities is the part of _______.
Answer
Answer: Cash and Cash Equivalents
Question 27.
Short term borrowings comes under _______.
Answer
Answer: Financing Activities
Question 28.
The cash flow statement explains the causes of ________ of cash.
Answer
Answer: Surplus / Deficit
Question 29.
Issue of shares on redemption of debentures will result into _______ of cash.
Answer
Answer: Noflow
Question 30.
Payment of dividend always come under _____ for all enterprises.
Answer
Answer: Financing
Question 31.
Sale and purchase of shares and securities come under _____ activities for financial enterprises.
Answer
Answer: Operating
Question 32.
Proceeds of insurance claims under norming business operations is known as _______.
Answer
Answer: Extraordinary Item
Question 33.
_______ dividend is declared and paid during the year.
Answer
Answer: Interim
Question 34.
Cheques and drafts are the part of cash ________.
Answer
Answer: Equivalents
Question 35.
Tax of dividend on shares is the part of _______ activity.
Answer
Answer: Financing.
One word Questions:
Question 36.
Mevo Ltd., a financial enterprise had advanced a loan of ₹ 3,00,000, invested ₹ 6,00,000 in shares of the other companies and purchased machinery for ₹ 9,00,000. It received dividend of ₹ 70,000 on investment in shares. The company sold an old machine of the book value of ₹ 79,000 at a loss of ₹ 10,000.
Compute Cash flows from Investing Activities. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer:
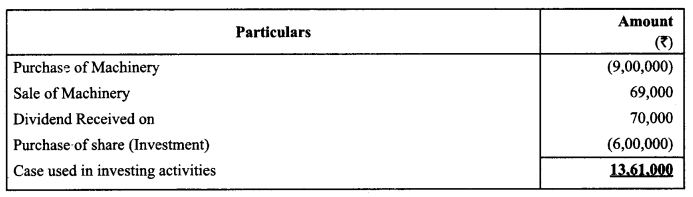
Note: As it is clearly mentioned that shares are purchased for investment. They have been treated as investing
activities.
Question 37.
Give the meaning of ‘Cash Equivalents’ for the purpose of preparing Cash Flow Statement. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer: “Cast equivalents” means short term highly liquid investments that are readily convertible into known amount of cash & which are subject to an in significant risk of changes in value.
For Ex-short term marketable securities.
The primary purpose of the statement of cash flows is to provide information about cash receipt, cash payments, and the net change in cash resulting from the operating, investing and financing activities of a company during the period.
Question 38.
What is meant by ‘Cash Flows? (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer: Cash Flows imply movement of cash in and out due to some non-cash items.
Question 39.
K Ltd., a manufacturing company obtained a loan of ₹ 6,00,000, advanced a loan of ₹ 1,00,000 and purchased machinery for ₹ 5,00,000. Calculate the amount of Cash Flow from financing and investing activities.
Ans.
Answer
Answer:
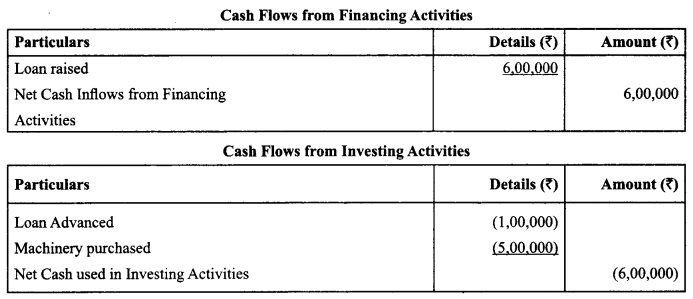
Question 40.
How will ‘commission received’ be treated while preparing cash-flow-statement? (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer: It will be treated as Cash flows from operating activities.
Question 41.
How is ‘dividend paid’ treated by a financial enterprise for the purpose of preparing cash flow statement?
Answer
Answer: Dividend paid is treated as a financing activity.
Question 42.
When can ‘Receipt of Dividend’ be classified as an operating activity State. Also give reason in support of your answer. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer: Receipt of dividend can be an operating activity for a financial company as it is a principal revenue generating activity.
Question 43.
What is meant by ‘Cash Flow Statement’? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer: A Cash Flow Statement is a statement that provides information about the historical changes in Cash & Cash Equivalents of an enterprise by classifying cash flows into Operating, Investing and Financing Activities.
Question 44.
What is meant by ‘Cash Flows’? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer: Cash Flows imply movement of cash in and out due to some non-cash items.
Question 45.
K Ltd., a manufacturing company obtained a loan of ₹ 6,00,000, advanced a loan of ₹ 1,00,000 and purchased machinery for ₹ 5,00,000. Calculate the amount of Cash Flow from financing and investing activities.
Answer
Answer:
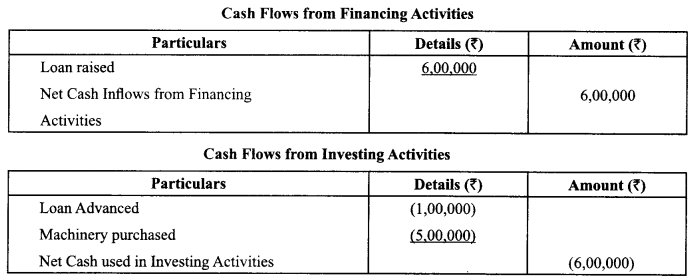
Question 46.
How will ‘commission received’ be treated while preparing a cash-flow-statement? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer: It will be treated as Cash flows from operating activities.
Question 47.
How is ‘dividend paid’ treated by a financial enterprise for the purpose of preparing cash flow statement? (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer
Answer: Dividend paid is treated as a financing activity.
Question 48.
M/s Mevo and Sons.; a bamboo pens producing company, purchased a machinery for ₹ 9,00,000.
It received dividend of ₹ 70,000 on investment in shares. The company also sold an old machine of the book value of ₹ 79,000 at a loss of ₹ 10,000. Compute Cash flow from Investing Activities (CBSE SP 2019-20)
Ans. Cash flow from Investing Activities
Answer
Answer:

Question 49.
Give any two examples of cash flows from operating activities.
Answer
Answer:
(i) Cash Sales
(ii) Cash Purchases
Question 50.
What is meant by ‘Financing Activities’ for preparing Cash Flow Statement? (CBSE 2019 Compt.)
Answer
Answer: Financing activities are the activities that result in change in capital or borrowings of the enterprise.
Question 51.
What is mean by investing activities for preparing Cash Flow Statement? (CBSE 2019 Compt.)
Answer
Answer: Investing activities (as per AS-3) are the acquisition and disposal of long term assets and other investments not included in cash equivalents.
Question 52.
State the primary objective of preparing Cash Flow Statement. (CBSE 2019 Compt.)
Answer
Answer: The primary objective of preparing Cash Flow Statement is to provide useful information about cash inflows and outflows of an enterprise during a particular period.
Question 53.
What is meant by‘Cash Flow Statement’? (CBSE 2019 Compt.)
Answer
Answer: Cash Flow Statement is a statement showing inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents during a particular period.
Question 54.
Cashier of Y Ltd. withdrew ₹ 2,00,000 from bank. Will this transaction result into inflow, outflow or no flow of cash? Give reason in support of your answer. (CBSE 2019 Compt.)
Answer
Answer: No flow of cash as there is no change in cash and cash equivalents.
Question 55.
Interest received and paid is considered as which type of activity by a finance company while preparing the cash flow statement. (CBSE 2018)
Answer
Answer: Operating Activity for both.
Question 56.
Under which type of activity will you classify ‘Rent received’ while preparing cash flow statement? (CBSE Sample Paper 2018-19)
Answer
Answer: Rent received is inflow of cash from Investing Activities.
Question 57.
Give any one example of cash inflows from operating activities other than cash receipts from sale of goods and rendering of services.
Answer
Answer: Royalties
Question 58.
P P Limited is Share Broker Company. G G Limited is engaged in manufacturing of packaged food. P P Limited purchased 5,000 equity shares of ₹ 100 each of Savita Limited. G G Limited also purchased 10,000 equity shares of ₹ 100 each of Savita Limited.
For the purpose of preparing their respective Cash Flow Statements, under which category of activities the purchase of shares will be classified by P P Limited and G G Limited? (CBSE Sample Paper 2017-18)
Answer
Answer:
(a) For P P Limited: Operating Activity
(b) For G G Limited: Investing Activity
Question 59.
Cash Flow Statement shows inflows and outflows of ‘Cash’ and ‘Cash Equivalents’ from various activities of an enterprise during a particular period. State one component of cash. (Compt. Delhi 2017)
Answer
Answer: Demand deposits with bank.
Question 60.
Give an example of an activity, which is a financing activity for every type of enterprise. (Compt. Delhi 2017)
Answer
Answer: Issue of shares.
Question 61.
Net increase in working capital other than cash and cash equivalents will increase, decrease or not change cash flow from operating activities. Give reason in support ofyour answer. (Delhi 2017)
Answer
Answer: Decrease.
Question 62.
‘Payment and Receipt of interest and dividend’ is classified as which type of activity while preparing cash flow statement? (Delhi 2017)
Answer
Answer: Payment of Interest and Dividend: Financing Activity Receipt of Interest and Dividend: Investing Activity
Question 63.
‘Cheques and drafts in hand’ are not considered while preparing cash flow statement. Why? (Delhi 2017)
Answer
Answer: Cheques and Drafts in hand are not considered while preparing cash flow statements as they are part of cash and cash equivalents only.
Question 64.
State any one advantage of preparing cash flow statement. (Delhi 2017)
Answer
Answer: It helps in short term financial planning.
Question 65.
Normally, what should be the maturity period for a short-term investment from the date of its acquisition to be qualified as cash equivalents? (Outside Delhi 2017)
Answer
Answer: 90 days/ 3 months.
Question 66.
State whether the following will increase, decrease or have no effect on cash flow from operating activities while preparing ‘Cash Flow Statement’ :
(i) Decrease in outstanding employees benefits expenses by ₹ 3,000
(ii) Increase in prepaid insurance by ₹ 2,000. (Compt. Delhi 2017)
Answer
Answer:
(i) Decrease
(ii) Decrease
Question 67.
Will ‘acquisition of machinery by issue of equity shares’ be considered while preparing ‘Cash Flow Statement’?
Answer
Answer: No.
Question 68.
The Goodwill of X Ltd. increased from ₹ 2,00,000 in 2013-14 to ₹ 3,50,000 in 2014-15. Where will you show the treatment while preparing Cash Flow Statement for the year ended 31st March 2015? (CBSE Sample Paper 2016, 2017)
Answer
Answer: Investing Activities.
Question 69.
Does movement between items that constitute cash or cash equivalents result into cash flow?
Answer
Answer: No flow of cash and cash equivalents.
Question 70.
‘An enterprise may hold securities and loans for dealing or trading purposes in which case they are similar to inventory acquired specifically for resale.’ Is the statement correct?
Answer
Answer: Yes
Question 71.
‘G Ltd.’ is carrying on a paper manufacturing business. In the current year, it purchased machinery for
7 30,00,000, it paid salaries of ₹ 60,000 to its employees; it required funds for expansion and therefore, issued shares of ₹ 20,00,000. It earned a profit of ₹ 9,00,000 for the current year. Find out cash flows from operating activities. (Delhi Compartment 2015)
Answer
Answer: ₹ 9,00,000 (as per indirect method and other information is not relevant)
Question 72.
Finserve Ltd. Is carrying on a mutual fund business. It invested ₹ 30,00,000 in shares and ₹ 15,00,000 in debentures of various companies during the year. It received ₹ 3,00,000 as dividend and interest. Find out cash flows from investing activities. (CBSE Sample Paper 2015)
Answer
Answer: Nil.
Question 73.
State with reason whether the issue of 9 % debentures to a vendor for the purchaser of machinery of ₹ 50,000 will result in inflow, outflow or no flow of cash while preparing cash flow statement. (CBSE Compartment Delhi 2014)
Answer
Answer: No flow of cash.
Question 74.
Interest received by a finance company is classified under which kind of activity while preparing a cash flow statement. (CBSE Sample Paper 2014)
Answer
Answer: Operating Activity.
Question 75.
While preparing cash flow statement of Sharda Ltd. Depreciation provided on fixed asset was added to the net profit to calculate cash flow from operating activities. Was the accountant correct in doing so? Give reason. (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer
Answer: Yes.
Question 76.
While preparing the cash flow statement of Alka Ltd. Dividend paid was shown as an operating activity by the accountant of the company. Was he correct in doing so?
Answer
Answer: No.
Question 77.
Asia Ltd. declared payment of dividend of₹ 50,000 on its equity shares. Mention with reason whether it is cash inflow, cash outflow or no cash flow.
Answer
Answer: No cash flow.
Question 78.
A company has issued bonus equity shares of ₹ 2,00,000. Mention with reason whether it is cash inflow,
cash outflow or no cash.
Answer
Answer: No cash flow.
Question 79.
Mention the case in which interest received (other than interest on calls in arrears) is treated as cash inflow from operating activities.
Answer
Answer: Cash inflow company.
Question 80.
State with reason whether deposit of cash into bank will result into inflow, outflow or no flow cash. (CBSE 2011 Delhi)
Answer
Answer: No cash flow equivalents.
We hope you found this CBSE Class 12 Accountancy Cash Flow Statement MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers helpful. If you have any questions about NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 11 Cash Flow Statement with Answers Pdf free download, please share them in the comment box below and we will get back to you at the earliest possible time.
Accountancy MCQ Class 12 Part 1 and Accounts MCQ Class 12 Part 2
- Accounting for Not for Profit Organisation Class 12 MCQ
- Accounting for Partnership: Basic Concepts Class 12 MCQ
- Reconstitution of Partnership Firm: Admission of a Partner Class 12 MCQ
- Reconstitution of Partnership Firm: Retirement / Death of a Partner Class 12 MCQ
- Dissolution of a Partnership Firm Class 12 MCQ
- Accounting for Share Capital Class 12 MCQ
- Issue and Redemption of Debentures Class 12 MCQ
- Financial Statements of a Company Class 12 MCQ
- Analysis of Financial Statements Class 12 MCQ
- Accounting Ratios Class 12 MCQ
- Cash Flow Statement Class 12 MCQ