These NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Ex 7.2 Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Exercise 7.2
Question 1.
In an issosceies triangle ABC, with AB = AC, the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C intersect each other at O. Join A to O show that:
(i) OB = OC
(ii) AO bisects ∠A
Solution:
(i) In ∆ABC,
We have given that
AB = AC
∴ ∠B = ∠C (Angle opposite to equal sides are equal)
or, \(\frac {1}{2}\) ∠B = \(\frac {1}{2}\) ∠C
∴ ∠1 = ∠2
Now in ∠OBC,
∠1 = ∠2
∴ OB = OC (Side opposite to equal angles are equal)
![]()
(ii) In ∆AOB and ∆AOC
AB = AC
OB = OC
∠B = ∠C
∴ \(\frac {1}{2}\) ∠B = \(\frac {1}{2}\) ∠B
or ∠3 = ∠4
Therefore, by S-A-S Congruency Condition,
∆AOB ≅ ∆AOC
∴ ∠BAO = ∠CAO (by C.P.C.T)
∴ AO is the bisector of ∠A.
Question 2.
In ∆ABC, AD is the perpendicular bisector of BC (see Fig. 7.30). Show that ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC.
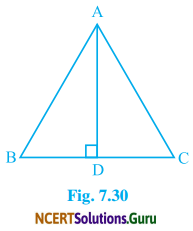
Solution:
In ∆ABD and ∆ACD
BD = CD (∵ AD bisects BC)
∠ADB = ∠ADC (Each 90°)
AD = AD (Common)
By S-A-S Congurency Condition,
∆ABD ≅ ∆ACD
Therefore, AB = AC (By C.P.C.T)
∴ ABC is an isosceles triangle.
![]()
Question 3.
ABC is an isosceles triangle in which altitudes BE and CF are drawn to side AC and AB respectively (see Fig. 7.31). Show that these altitudes are equal.
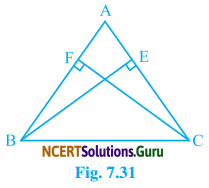
Solution:
In ∆ABE and ∆ACF,
∠A = ∠A (Common)
∠AEB = ∠AFC (each 90°)
AB = AC (Given)
By, A-A-S Congruency Condition
∆ABE = ∆ACP
Therefore, BE = CF (By C.P.C.T)
Question 4.
ABC is a triangle in which altitudes BE and CF to sides AC and AB are equal (see Fig. 7.32). Show that
(i) ∆ABE ≅ ∆ACF
(ii) AB = AC, i.e. ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle.
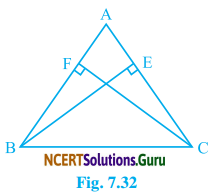
Solution:
(i) ∆ABE and ∆ACF,
BE = CF (Given)
∠A = ∠A (Common)
∠AEB = ∠AFC (Each 90°)
By A-A-S Congruency Condition
∆ABE = ∆ACF
(ii) Since ∆ABE ≅ ∆ACF
So, AB = AC (By C.P.C.T.)
or, ∆ABC is an isosceles triangle.
![]()
Question 5.
ABC and DBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC (see Fig. 7.33). Show that ∠ABD = ∠ACD.
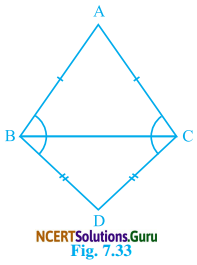
Solution:
In ∆ABC,
AB = AC
∴ ∠ABC = ∠ACB …….(i)
(Angle opposite to equal sides of a ∆ are equal)
Again, In ∆DBC
DB = DC
∠DBC = ∠DCB ……(ii)
(Angle opposite to equal sides of a ∆ are equal)
Adding equation (i) and (ii)
∠ABC + ∠DBC = ∠ACB + ∠DCB
or ∠ABD = ∠ACD.
Question 6.
∆ABC is an isosceles triangle in which AB = AC. Side BA is produced to D such that AD = AB (see Fig. 7.34). Show that ∠BCD is a right angle.
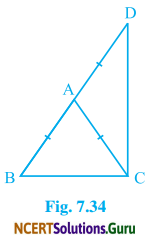
Solution:
In ∆ABC,
AB = AC
∠ABC = ∠ACB ……(i)
(Angles opposite to equal sides of a ∆ABC)
Now, In ∆ACD,
AC = AD
∠ACD = ∠ADC ……(ii)
(Angles opposite to equal sides of ∆ACD)
Now, ∠BAC + ∠CAD = 180° ……(iii) (Linear pair)
Also, ∠CAD = ∠ABC + ∠ACB (Exterior angle of ∆ABC)
∠CAD = 2∠ACB …….(iv)
From equation (i),
∠ABC = ∠ACB
and ∠BAC = ∠ACD + ∠ADC (Exterior angle of ∆ADC)
∠BAC = 2∠ACD …….(v)
(From equation (ii), ∠ACD = ∠ADC)
From equation (iii) we have,
∠BAC + ∠CAD = 180°
⇒ 2∠ACD + 2∠ACB = 180° (From equation (iv) and (v))
⇒ 2(∠ACD + ∠ACB) = 180°
⇒ 2(∠BCD) = 180°
⇒ ∠BCD = 90°
![]()
Question 7.
ABC is a right-angled triangle in which ∠A = 90° and AB = AC. Find ∠B and ∠C.
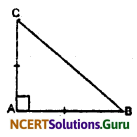
Solution:
In ∆ABC,
AB = AC
∴ ∠B = ∠C (Angle opposite to equal sides of ∆ABC)
Now, ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° (Angle sum property)
or, 90° + ∠B + ∠B = 180° (∵ ∠A = 90° and ∠B = ∠C)
or, 2∠B = 90°
∴ ∠B = 45°
Therefore, ∠B = ∠C = 45°.
![]()
Question 8.
Show that the angles of equilateral triangles are 60° each.
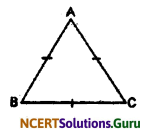
Solution:
In ∆ABC,
AB = BC = AC (Because ABC is an equilateral triangle)
∴ ∠C = ∠A = ∠B (Angle opposite to equal sides of ∆ABC)
Now, ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° (Angle sum property of ∆)
or, ∠A + ∠A + ∠A = 180° (∵ ∠A = ∠B = ∠C)
or, 3∠A = 180
Therefore, ∠A = 60°
Again, ∠A = ∠B = ∠C
∴ ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°
Therefore, each angle of an equilateral ∆ is 60°.