These NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts to help students while preparing for their exams.
Synthetic Fibres and Plastics NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3
Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
Page 41-42
Question 1.
Explain why some fibres are called synthetic.
Answer:
Some fibres are called synthetic fibres because they are man-made. These fibres are made by the combination of different types of chemicals in industries and their properties are also different from those of the natural fibres. Some of the examples of synthetic fibres are nylon, rayon, acrylic, polyester, etc.
Question 2.
Mark (✓) the correct answer. Rayon is different from synthetic fibres because
a. it has a silk-like appearance.
b. it is obtained from wood pulp.
c. its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres.
Answer:
b. it is obtained from wood pulp.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
a. Synthetic fibres are also called …………… or …………… fibres.
b. Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw material called ……………
c. Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a ……………
Answer:
a. artificial, or man-made
b. petrochemicals,
c. polymer
Question 4.
Give examples which indicate that nylon fibres are very strong.
Answer:
Nylon is used for making parachutes. A parachute needs to be strong as it has to withstand high speed wind and huge amount of air pressure. Nylon ropes are used by mountaineers. A mountaineer’s life highly depends on the strength of ropes he is using. These examples show that nylon fibres are very strong.
Question 5.
Explain why plastic containers are favoured for storing food.
Answer:
Plastic does not react with most of the substances. Hence, food kept in plastic container remains fresh for longer duration. Due to this, plastic containers are preferred for storing food.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic.
Answer:
| Thermoplastic | Thermosetting Plastic |
| 1. Long, straight-chained compounds. | 1. Cross-linked compounds. |
| 2. Formed by addition polymerisation. | 2. Formed by condensation polymerisation. |
| 3. Low strength compared to thermosetting plastics. | 3. More strength compared to thermoplastics. |
| 4. Can be processed again and again. | 4. Cannot be processed again or recycled. |
| 5. E.g., Polyethylene. | 5. E.g., Bakelite, epoxy. |
Question 7.
Explain why the following are made up of thermosetting plastics.
a. Saucepan handles
b. Electric plugs/switches/plugboards
Answer:
a. Thermosetting plastic is fire-resistant and can withstand very high temperatures. Due to this, saucepan handles are made up of thermosetting plastic. Such handles do not heat up during cooking,
b. Thermosetting plastic is a bad conductor of electricity and heat. Hence, electric plugs, switches and plugboards are made up of thermosetting plastic.
Question 8.
Categorise the materials of the following products into ‘can be recycled’ and ‘cannot be recycled’:
Telephone instruments, plastic toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ballpoint pens, plastic bowls, plastic covering on electrical wires, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Answer:
- Can be recycled: plastic toys, ballpoint pens, plastic bowls, plastic chairs, carry bags, plastic covering on electrical wires.
- Cannot be recycled: Cooker handles, telephone instruments, electrical switches.
Question 9.
Rana wants to buy shirts for summer. Should he buy cotton shirts or shirts made from synthetic material? Advise Rana, giving your reason.
Answer:
A shirt made from synthetic materials does not allow air to pass through it. On the other hand, a shirt made from cotton allows air to pass through it. Also, water from cotton evaporates easily, causing a cooling effect while a synthetic fibre retains moisture leading to humidity in summers. Hence, a cotton shirt keeps the body temperature lower. Hence, a cotton shirt is more comfortable in summers than a shirt made from synthetic material. Therefore, Rana should buy a cotton shirt.
Question 10.
Give examples to show that plastics are non-corrosive in nature.
Answer:
We know that acids and bases are corrosive in nature. Nowadays, many acids and bases are stored in plastic containers. This is possible because of non-corrosive nature of plastic. A plastic chair does not get rusted like an iron chair does. This also happens because of the non-corrosive nature of plastic.
Question 11.
Should the handle and bristles of a toothbrush be made of the same material? Explain your answer.
Answer:
Purpose of the handle of a toothbrush is different from the purpose of bristles of the toothbrush. The handle needs to be strong and less flexible. The bristles need to be highly flexible, soft yet durable. Hence, bristles need to be made up of a different material than the material of toothbrush handle.
Question 12.
‘Avoid plastics as far as possible’. Comment on this advice.
Answer:
We know that plastic is non-biodegradable. This means that plastic waste keeps getting accumulated in our environment. Accumulation of plastic waste is creating a huge problem for us. Hence, we should avoid plastic as far as possible. We should switch over to biodegradable alternatives wherever possible. For example, we should use shopping bags made up of jute or cloth instead of plastic. If plastic is burnt it releases poisonous gases and the plastic bags thrown in the garbage dump are swallowed by animals. They choke their respiratory system and this causes fatalities in animals.
![]()
Question 13.
Match the terms of column A correctly with the phrases given in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Polyester | (a) Prepared by using wood pulp |
| (ii) Teflon | (b) Used for making parachutes and stockings |
| (iii) Rayon | (c) Used to make non-stick cookwares |
| (iv) Nylon | (d) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily |
Answer:
(i) → (d),
(ii) → (c),
(iii) → (a),
(iv) → (b)
Question 14.
‘Manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping conservation of forests’. Comment.
Answer:
Synthetic fibres have replaced natural fibres for most uses. It has resulted in reducing our dependency on natural fibres. Many natural fibres come from plants and hence plants need to be cut down to obtain these fibres. Less demand for natural fibres means there is a reduced need to cut down the trees. It has helped in conservation of forests. Hence, it can be said that manufacturing synthetic fibres is actually helping conservation of forests.
Question 15.
Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Answer:
For this, take a small piece of thermoplastic, some copper wires, two electric cells and an electric bulb (from torch).
- Connect the bulb with the battery and attach the thermosetting plastic to wires to make a circuit.
- It is observed that the bulb does not glow.
- When thermosetting plastic is replaced with a metal rod in the circuit, the bulb begins to glow.
- This shows that thermosetting plastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Caution: Do this activity in the presence of your teacher or parent.
NCERT Extended Learning Activities and Projects
Question 1.
Have you heard of the campaign: “Say No to Plastics”. Coin a few more slogans of this kind. There are certain governmental and non-governmental organisations who educate general public on how to make a wise use of plastics and develop environment friendly habits.
Find out organisations in your area which are carrying out awareness programmes. If there is none, form one.
Hint.
Related slogans:
a. “Don’t laminate the earth!”
b. “Eating plastic, animals died; seeing plastic, nature cried. So, say no to plastics!”
c. “Plastics are dangerous which spoil the river. After some days we will shiver.”
There are many organisations which carry out awareness programmes such as Bharat Seva Sangh [established in 2000], Sewak (established in 1998), Aarti (established in 2009), MUSS (Manav Uthhan Seva Sansthan) (established in 2001).
![]()
Question 2.
Organise a debate in the school. Children may be given an option to role play as manufacturers of synthetic fabrics or those of fabrics from natural sources. They can then debate on the topic ‘My Fabric is Superior’.
Hint.
The clothes which we wear are made up of fabrics. Fabrics are made from fibres obtained from natural or artificial sources. Fibres are obtained from four main sources: animal (wool, silk), plant (cotton, flax, jute), mineral (asbestos, glass fibre) and synthetic (nylon, polyester, acrylic). Fibres are also used for making a large variety of household articles.
Question 3.
Visit five families in your neighbourhood and enquire about the kind of clothes they use, the reason for their choice and advantages of using them in terms of cost, durability and maintenance. Make a short report and submit it to your teacher.
Hint:
Do it yourself.
Question 4.
Devise an activity to show that organic waste is biodegradable while plastic is not.
Hint:
Activity: Collect garbage from your house before it is thrown into the dustbin. Separate the garbage into two groups.
In group 1, include wastes such as polythene bags, chips packets, empty plastic bottles, plastic toys, etc. In group 2, include only kitchen wastes like peels of fruits and vegetables, waste food, newspaper and garden wastes like dead leaves and other plant parts. Bury these materials separately in two pots and label them as A and B. Remove the top soil after one week and check the status of the garbage. Then approximately after four weeks, check the condition of the garbage again.
It will be observed that the waste in pot B decomposes, while the waste in pot A does not decompose.
This shows that the waste (plastic) kept in pot A is non-biodegradable, while the waste (organic waste) kept in pot B is biodegradable.
Activity 1
Objective: To show that the nylon thread is stronger than cotton, wool, silk and polyester threads.
Materials Required: Different threads (cotton, wool, silk, nylon and polyester), iron stand and pan.
Procedure:
- Take an iron stand with clamp.
- Take a cotton thread of about 60 cm length.
- Tie it to the clamp so that it hangs freely from it as shown in the figure.
- At the free end, suspend the pan so that weight can be placed on it.
- Add weight one by one till the thread breaks.
- Note down the total weight required to break the thread. This weight indicates the strength of the fibre.
- Repeat the same activity with threads of wool, silk, polyester and nylon.

Observation: It can be observed that more weight is required to break the nylon thread in comparison to wool, silk, cotton and polyester threads.
Conclusion: Nylon thread is stronger than any other thread.
i. Polyester: Polyester is made up of repeating units of a chemical called ester. The fibres of polyester do not get wrinkled easily, remain crisp and easy to wash. They are used for making clothes, curtains and dress materials. Terylene, when blended with cotton, is called terry cot while with wool it gives terry wool. Clothes made up of such polymers are convenient to use.
PET (Polyethylene terephthalate) is another example of a polyester. It is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires and many other items. Polyester fabrics do not wrinkle easily and are easy to wash.
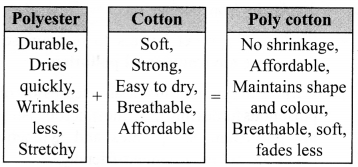
iv. Acrylic: Acrylic resembles wool and hence is also called as synthetic wool. It is cheaper and more durable than wool and is easier to wash and maintain.
Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres
- Synthetic fibres are cheaper, stronger and more durable than natural fibres.
- These are easy to maintain, easy to wash, dry up in less time and readily available.
- These fibres possess unique characteristics which make them popular dress materials.
![]()
Activity 2
Objective: To study and compare the water absorbing property of natural and synthetic fibres.
Materials Required: Two types of cloth (cotton and polyester), water, and mug.
Procedure:
- Soak the two cloth pieces in different mugs containing same amount of water.
- Now, take out the cloth pieces after five minutes and spread them in the Sun.
- Compare the amounts of water remaining in the mugs.
- Also compare the dryness of both the cloth pieces after keeping in Sun for a few minutes.
Observation: It can be observed that the cotton cloth absorbs more water than the polyester cloth. Also, polyester dries up quickly but cotton does not.
Conclusion: Synthetic libres absorb much less water than the natural fibres.
Plastics: Plastic too is a polymer. However, arrangement of units is different in different types of plastics. In some plastics, the individual units are linked in a linear fashion. In some other plastics, the individual units are cross-linked. Plastic is easily moutdable, recyclable, reusable, colourable, can be melted, rolled into sheets or drawn into wires.
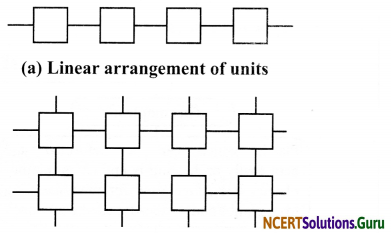
(b) Cross-linked arrangement of units:
Plastic is used in making toys, suitcase, bags, cabinets, brush, chairs, tables and many other countless items. Polythene (Poly + ethene) is one of the most famous examples of plastic, which is used in the manufacturing of carry bags.
Plastics as Materials of Choice: Due to various qualities, plastics are used in our everyday life.
- Plastic is non-reactive: Plastics do not react with water and air due to which they do not get rusted like iron. They are not corroded easily. So, they are used to store various kinds of materials, including many chemicals.
- Plastic is light, strong, cheaper and durable: They are generally cheaper than metals. Hence, they are widely used in industry and household articles.
- Plastic is a poor conductor of heat: Plastics are poor conductors of heat. They are therefore used in making handles of screwdrivers and cooking vessels and in making containers for microwave oven.
- Plastic is poor conductor of electricity: Plastics are poor conductors of electricity and are used in making a cover for electric wires, cables and appliances. Electric switches are made from bakelite.
Plastic and the Environment:
i. Biodegradable: A material which can be decomposed by microbes is called a biodegradable material, e.g., jute, cotton, paper, leftover food, etc.
ii. Non-biodegradable: A material which cannot be decomposed by microbes is called a non-biodegradable material, e.g., plastic, iron, copper, etc.
Plastics take several years to decompose, thus cause environmental pollution.
Burning of synthetic materials releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution. So, plastics and synthetic fibres are not environment-friendly.
Nuisance of Plastic Bags
- Plastic bag keeps on accumulating in the environment.
- It chokes drains leading to waterlogging.
- A stray animal can die if it accidentally swallows a plastic bag.
How to tackle the problem of plastic waste?
i. Avoid the use of plastics as far as possible.
ii. Follow the 5R principle i.e., Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover and Refuse.
Recycle

iii. Use recyclable plastic or use shopping bags of cloth or jute.
iv. Do not throw plastic bags on roads or in drains.
v. Reuse plastic containers for keeping household items.
Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Additional Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are natural fibres? Give examples.
Answer:
The fibres obtained from plants and animals are called natural fibers. For example cotton, silk, jute, etc.
Question 2.
Define polymer.
Answer:
A polymer is a large molecule formed by the combination of many small molecules, each of which is called a monomer.
Question 3.
Name a natural polymer.
Answer:
Cellulose.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the monomer units of cellulose?
Answer:
Cellulose is made up of a large number of glucose units.
Question 5.
Name the fibre having properties similar to that of silk.
Answer:
Rayon.
Question 6.
What is polyester?
Answer:
The polymer made up of the repeating units of ester is called polyester.
Question 7.
What is the full form of PET?
Answer:
Polyethylene terephthalate.
Question 8.
What is the full form of PVC?
Answer:
Polyvinyl chloride.
Question 9.
What are plastics?
Answer:
The plastics are a mouldable synthetic material made from a wide range of organic polymers such as polyethylene, PVC, nylon, etc.
Question 10.
What are the two types of arrangement of units in plastic?
Answer:
Linear linking and cross-linking.
![]()
Question 11.
Which synthetic fibre is also known as ‘artificial wool’?
Answer:
Acrylic.
Question 12.
Why is teflon used as a tape for sealing purposes?
Answer:
Because of its toughness, teflon is used as a tape for sealing purposes.
Question 13.
Name the first fully synthetic fibre.
Answer:
Nylon.
Question 14.
Why is nylon used for making parachutes?
Answer:
Nylon is used for making parachutes because it is very strong, elastic and light.
Question 15.
What are petrochemicals?
Answer:
Petrochemicals are the raw materials which are further used to make synthetic fibres.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How can polythene carry bags be harmful for animals?
Answer:
Polythene carry bags are thrown here and there after being used. Stray cattle consume them. In this case, it can choke their respiratory system and damage their stomach. It can even cause their death.
Question 2.
Give two disadvantages of synthetic fibres.
Answer:
- Most synthetic fibers catch fire very easily. Therefore, it is not advisable to wear them near a source of fire,
- Most synthetic fibers absorb very little moisture. They become sticky when the body sweats, which makes them uncomfortable to wear in hot weather.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a short note on acrylic.
Answer:
Acrylic resembles wool and hence is also called synthetic wool. It is cheaper and more durable than wool and is easier to wash and maintain. Acrylic is less expensive and easily available.
Question 4.
What is the difference between nylon and rayon?
Answer:
| Rayon | Nylon |
| 1. It was the first synthetic fibre. | 1. It was the first truly synthetic fibre. |
| 2. Rayon is made from wood pulp. | 2. Nylon is made from coal, water and air. |
| 3. Rayon is used for making curtains, bedsheets, etc. | 3. Nylon is used for making socks, ropes, toothbrushes, parachutes, etc. |
Question 5.
What do you mean by biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials? Explain with examples.
Answer:
- Biodegradable materials: A material which can be decomposed by the action of microbes is called a biodegradable material, e.g., jute, cotton, paper, leftover food, etc.
- Non-biodegradable materials: A material which cannot be decomposed by the action of microbes is called a non- biodegradable material, e.g., plastic, iron, copper, etc.
Question 6.
What is 5 R principle?
Answer:
5 R stands for:
- Reduce the use of non-biodegradable things.
- Reuse the things again and again.
- Use the thing which can be recycled.
- Recover the lacking substance.
- Refuse the plastics and other harmful articles.
Question 7.
Why has the government banned the use of polythene bags?
Answer:
Polythene or plastic bags are non-biodegradable. It means that they cannot be decomposed or recycled by the action of microorganisms. Besides this, an improper disposal of polythene leads to the following environmental problems:
- Soil and water pollution.
- Blockage and choking of drains and sewer lines.
- Death of animals that chew these polythene bags along with any food.
![]()
Question 8.
Why do mountaineers use nylon ropes for climbing the mountains?
Answer:
Mountaineers use nylon ropes for climbing the mountains because nylon is a high strength fibre and does not break easily. It has capacity to bear weight and helps the mountaineers to climb.
Question 9.
What is the chemical nature of polyester? What are polycot and poly wool?
Answer:
Polyester is actually made by the repeating units of a chemical called ester. Esters are the chemicals which give a characteristic fruity smell. Fabrics are sold by the names like poly cot, poly wool, terry cot, etc. As the name suggests, these are made by mixing two types of fibres. Polycot is a mixture of polyester and cotton while poly wool is a mixture of polyester and wool.
Question 10.
Why is polyester quite suitable for making dress materials?
Answer:
Fabric made from polyester does not get wrinkled easily. It remains crisp and is easy to wash. So, it is quite suitable for making dress material.
Question 11.
Why has artificial wool become more popular than natural wool?
Answer:
Artificial wool is prepared from a synthetic fibre called acrylic. The material obtained from natural sources is quite expensive whereas materials made from acrylic are relatively cheaper and available in a variety of colours. Synthetic fibres are more durable and affordable which makes them more popular than natural fibres.
Question 12.
Give three advantages of polythene over natural materials.
Answer:
Three advantages of polythene over natural materials are:
- It is light, strong and durable.
- It can be rolled into sheets.
- It does not react with water and air.
Question 13.
Why is a plastic bucket preferred over an iron bucket?
Answer:
Plastic bucket is preferred over an iron bucket because iron is reactive and it oxidises upon reaction with oxygen and moisture to form rust while plastic is non-reactive and does not form any rust.
![]()
Question 14.
Name two polyester fabrics and write their uses.
Answer:
Terylene and PET are polyester fabrics:
- Terylene is a popular polyester. It can be drawn into very fine fibres that can be woven like any other yam.
- PET is a very familiar form of polyester. It is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires and many other useful products.
Question 15.
Why should we not wear synthetic clothes while working in kitchen or in a laboratory?
Answer:
Synthetic fibres melt on heating. If the clothes catch fire, it can be disastrous. The fabric will melt and stick to the body of the person wearing it causing bums. We should, therefore, not wear synthetic clothes while working in the kitchen or in a laboratory.
Question 16.
Differentiate between natural and synthetic fibres.
Answer:
| Natural Fibres | Synthetic Fibres |
| a. Natural fibres are obtained from plants and animals. | a. Synthetic fibres are made by human beings by the chemical processing of petrochemicals. |
| b. Example: Cotton, wool, silk, etc. | b. Example: Rayon, nylon, polyester and acrylic. |
Question 17.
Describe the characteristic features of the synthetic fibres.
Answer:
Following are the characteristic features of synthetic fibres:
- Raw materials: All synthetic fibres are made from chemicals. They are prepared by a number of processes using raw materials of petroleum family called petrochemicals.
- Strength: Synthetic fibres are quite strong, e.g., nylon.
- Durability: Synthetic fibres are quite durable. They do not wither easily.
- Soak less water: Synthetic fibres absorb small quantities of water and lose it quickly. Hence, they dry up very soon.
- Availability and cost: Synthetic fibres are less expensive and readily available.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the discovery and unique features of nylon.
Answer:
Nylon was synthesized in 1935 by Wallace Carothers in DuPont’s research laboratory. The term ‘nylon’ has been derived from the letters of ‘New York’ and ‘London’. No ingredient from plant or animal source was used in making nylon. It was made from coal, water and air. Hence, nylon is called the first truly synthetic fibre. Some of its unique features are as follows:
- Nylon is strong, light and elastic.
- It is lustrous and easy to wash.
- Nylon is used in many articles, like socks, bags, toothbrushes, ropes, sneakers, parachutes, etc.
- For the same thickness, a nylon thread is stronger than a steel wire.
Question 2.
Explain different types of plastics and their uses.
Answer:
Different types of plastic and their uses are as follows:
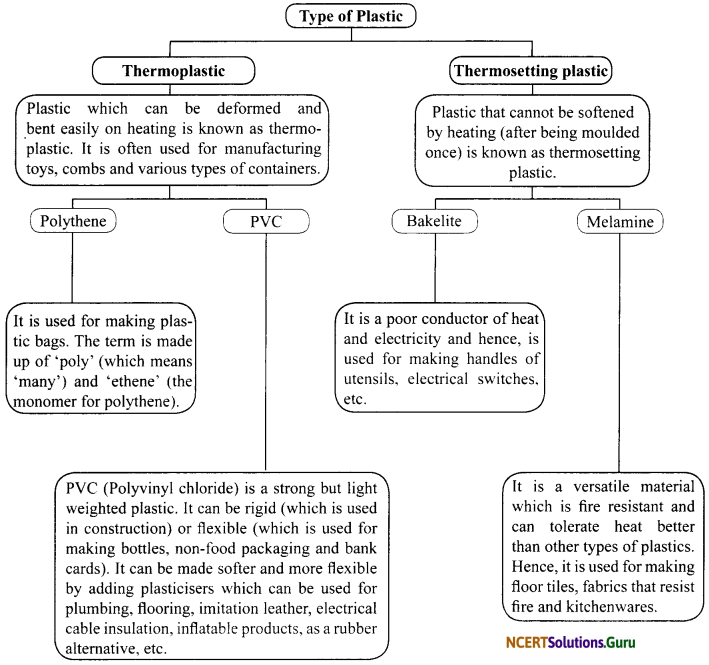
a. Thermoplastic: Some plastics get easily deformed on heating, and can be easily bent and re-shaped. They are called thermoplastics. Polythene and PVC are examples of such plastics. Thermoplastic is used for making combs, toys, buckets, mugs, etc.
b. Thermosetting Plastic: Some plastics do not get deformed on heating, and cannot be re-moulded into a new shape. Such plastics are called thermosetting plastics. Bakelite and melamine are examples of thermosetting plastic. Bakelite is used for making electrical switches and electrical switchboards because it is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. Melamine is resistant to fire and is hence used for making utensils.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the reasons for the popularity of plastic?
Answer:
Following are the reasons for the popularity of plastic:
a. Plastic is non-reactive: Unlike iron, plastic does not react with air to form rust. Due to this, plastic has replaced iron from many articles. Plastic does not react with many chemicals and hence, plastic containers are used for keeping many materials and chemicals.
b. Plastic is light, strong and durable: Plastic is light-weighted, strong and durable. Plastic chairs have replaced wooden chairs in most of the households. Wooden crates have been replaced by plastic crates for keeping milk and cold drinks. Most of the warehouses now use plastic pellets for keeping goods.
c. Plastic is a poor conductor of heat and electricity: Because of poor conductivity to heat and electricity, plastic is used for making switches and many components of electrical appliances. Handles of utensils are made up of plastic because such handles do not heat up.
Question 4.
Suggest some methods to minimise or limit the consumption of plastics.
Answer:
Some ways to limit plastic consumption are:
- Reducing the use of plastics. Whenever possible, use paper or jute bags instead of plastic or jute bags.
- Reusing it for some other purpose, thereby decreasing its consumption.
- Recycling of plastic. It requires the plastic to be collected, sorted, chopped, melted and remoulded.
Question 5.
Make a table to show the time taken by various types of wastes to degrade.
Answer:
According to the research, following is the estimated time taken by some everyday items to decompose in landfill sites:
|
Type of waste |
Time taken to degenerate |
| Plastic bottles | 70-450 years |
| Plastic bag | 500-1000 years |
| Tin can | Around 50 years |
| Leather shoes | 25-40 years |
| Cotton | 1-5 months |
| Rope | 3-14 months |
| Cigarette | 1-12 years |
| Milk packet (tetra) covers and drink packets | 5 years |
| Nylon clothes | 30-40 years |
| Sanitary napkins and children diapers | 500-800 years |
| Glass bottles | 1,000,000 years y |
Picture-Based Questions
Question 1.
Draw a diagram to show the:
a. Linear arrangement of units in plastic.
b. Cross-linked arrangement of units in plastic.
Answer:
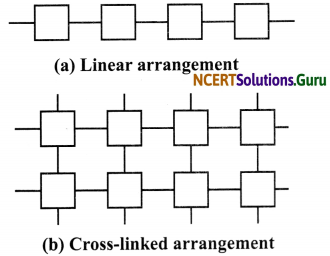
![]()
Question 2.
Observe the given articles and name the fibrous material they are made from.
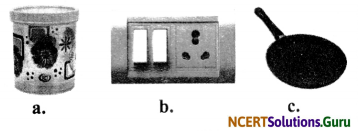
Answer:
a. Plastic food container
b. Bakelite switch
c. Teflon-coated pan