These NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Practical Geometry InText Questions and Answers are prepared by our highly skilled subject experts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 14 Practical Geometry InText Questions
NCERT In-text Question Page No. 286
Question 1.
In Step 2 of the construction using ruler and compasses, what would happen if we take the length of radius to be smaller than half the length of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) ?
Answer:
In case we take the radius smaller than half of the length of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\), the arcs will not intersect each other at two points P and Q.
NCERT In-text Question Page No. 289
Question 1.
In Step 2 above, what would happen if we take radius to be smaller than half the length BC?
Answer:
If we take radius to be smaller than half of BC, the arcs drawn with centres B and C will not intersect each other.
![]()
NCERT In-text Question Page No. 290
Question 1.
How will your construct at 15° angle?
Answer:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Construct an angle ∠ABC of 60°.
Step II: Bisect ∠ABC to get an angle of 30°
i. e. ∠ABD = 30°.
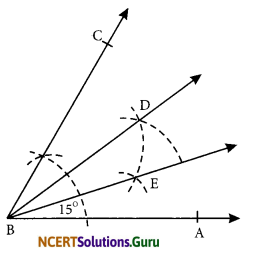
Step III: Bisect ∠ABD, such that \(\overline{\mathrm{BE}}\) is bisector of ∠ABD.
Thus, ∠ABD = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)(30°) = 15°.
NCERT In-text Question Page No. 291
Question 1.
How will you construct a 150° angle?
Answer:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw a line I and mark a point O on it.
Step II: With centre O and a convenient radius, draw an arc intersecting I at A.
Step III: With the same radius and centre at A, draw an arc to cut the first arc at B.
Step IV: Again with the same radius and centre at B, draw another arc to intersect the
first arc at C.
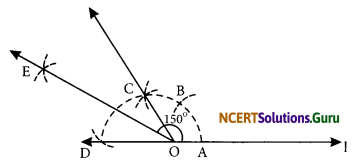
Step V : Once again with the same radius and centre at C, draw an arc to cut the first are at D.
Step VI: Now, bisect ∠COD, such that ∠COE = ∠EOD = 30°.
Step VII: Since, 150° = 120° + 30°, therefore ∠AOC + ∠COE = ∠AOE. Thus, ∠AOE is the required angle whose measure is 150°.
![]()
Question 2.
How will you construct a 45° angle?
Answer:
Steps of construction :
Step I: Construct an angle of 90° as shown in
the figure. ∠POQ = 90°.
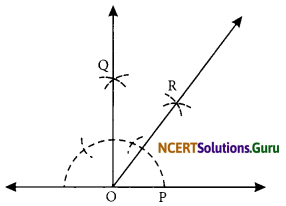
Step II: Draw OR, the angle bisector of ∠POQ such that \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)– [∠POQ] = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (90°) = 45° or ∠POR = 45°