Detailed, Step-by-Step NCERT Solutions for 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing Questions and Answers were solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines covering each topic in chapter to ensure complete preparation.
Marketing NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11
Marketing Questions and Answers Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11
Question 1.
Explain the advantages of branding to marketers of goods and services.
Answer:
Advantages of Branding to Marketers
(i) Enables marking Product differantiation Branding helps a firm in distinguishing its product from that of its competition. This enables the firm to secure and control the market for its products;
(ii) Helps in advertising and display programmes A brand aids a firm in its advertising and display programs. Without a brand name, the advertiser can only create awareness for the generic product and can never be sure of the°sale for his product;
(iii) Differential Pricing Branding enable a firm to charge different price for its products than that charged by its competition. This is possible because if, customers like a brand and become habitual of it, they do not mind paying a little higher for it.
(iv) Ease in introduction of new product: If a new product is introduced under a known brand, it enjoys the reflected glory of the brand and is likely to get off to an excellent starts. Thus, many companies with established brand names decide to introduce new products in the same name.
For example, Foods Specialities Ltd. has a has a succesful brand Maggie noddles. It extended this name to many of its new products introduced such as Tomato Catch Up, Soups, etc. Similarly Samsung extended the brand name of its Television to Washing Machines and other durable products, like Microwave oven etc.
![]()
Question 2.
List the characteristics of a good brand name.
Answer:
Branding is a managerial function. It is general term covering various activities, such as giving a brand name to a Resigning a brand mark, establishing it and popularising it. In selecting a good brand name various aspects requires careful consideration. The following are some general considerations which must be considered for selecting and deciding the brand name of the product.
1. Simple, Short and SweetThe brand name should be simple so that it could be easily understandable and short so that it could be easy to rememeber and sweet appealing to eyes, ears and brain, for example Tata, Bata, Dalda, Nirma, Maruti, Lux, Hamam, Surf, Rin, Sony etc.
2. Easy Pronounciation : The brand name should be so easy to pronounce as no difficulty faced by the children, youngsters, old, woman, literate, illiterate, rural and urban population. It could be easily pronounced in different languages, for example Maggie Lipton, Surya; BPL, LG, DCM etc.
3. Recognisable : The brand name should not be imitation of other and other cannot copy it easily. It should be original and distinctive of the product and the manufacturers. For example Godrej, Liberty, HMT, Philips, Nerolac, Titan, Colgate, Limca etc.
4. Suggestive : The brand name should go along with the functions, benefits and the special qualities of the product. For example Goodnight, Allout, Milkmaid, Keshnikhar, Aquaguard, Sunsilk, Neem , soap, Dhara, Frooti, Hotline, Symphony etc.
5. Economical : A good brand name should be economic to reproduce. No more expenditure should be incurred on printing, writing, or exhibiting the same. Certain names can be easily designed and graphed, advertised and promoted. For example Nirma, Maggie, Surf, Rin, Everest, Dev Darshan, Atlas, Hero etc.
6. Regally Protectable The brand should be such which can be easily registered under the Trade and Merchandise Act 1958. Section 11 and 12 of Trade and Merchandise 1958 lay down certain conditions. Any name selected cannot be registered as trademark. The name should 4 not be too closely associated with an existing trademark.
7. Helpful in advertisingThe name and mark of brand should be,skillfully selected so that it may be easily used in advertising and should make the advertisement more attractive such as Nirma, Milkfood.
8. Far from obescence Any type of vulgarity should not be demonstrated through the brand. It should not harm the emotions of any individual group or religion. Such as Bakeman, Britannia etc.
9. Heart touching : The name of brand, its mark and picture should be of such nature as to merge with the mind and heart of the viewer and could impress him. Such as Shahnaz, Ebony, Galaxy etc.
![]()
10. Suitable to buyers The brand name should be such which suits the buyers. For exampleWomen, consumers are more attracted by feminine names e.g. Lakme (Cosmetics), Lady Birds (cycle) and men to masculine ones e.g. Ruf and Tuf (Jeans). Axe (deodorant) etc, Above points makes it clear that the home or mark of a brand must be selected only after due consideration.
The goodwill of the firm and success of marketing efforts of a firm gains popularity among customers, the demand for that product goes very high. Now -a-days we fi nd many examples of product success because of brand popularity.
Question 3.
What is the societal concept of marketing?
Answer:
The marketing concept, as described in the proceeding section cannot be considered as adequate if we look at the challenges posed by social problem like environmental polluton, deforestation, shortage of resourse, population explosion and inflation. It is so because any activity which satisfies at large cannot be justified. The business orientation should therefore not be short -signted to serve only consumers needs.
It is an undisputed fact that a company’s survival does not depend upon its consumers alone, but a diverse set of segments like the government, religious leaders social activists, NGO’s, Media etc.
Hence, earning the satisfaction of these segments is also an imperative as they add to the power of the brand by word of mouth. The social concern adds to the strength of the brand. Corporate that embraced the deepest social value, have been successful in building powerful brand and eventually, robust customer relationship.
The area of corporate social justice fall under two broad catagories. The issue such as are the nutrition of children, child care, old-age homes, amelioration of hunger, offering aid to those affected by natural calamities etc. needing instant attention with a humanitarial perspective, comes under the first category.
![]()
The issues that contribute to making society at pleasant place to live in the long run, may be grouped under the second catagory. Health awareness and aid, education, environmental protection. Women’s employment and empowerment, preventing unjust discrimination (an the basis of caste, community, religion, ethnicity, race and sex), eradication of poverty through employment, preservation of culture, value and ethics contribution to reasearch etc. come under the second category.
The societal marketing concept holds the task of any organisation is to identify the needs and wants of the target market and deliver the designed satisfaction in an effective and efficient manner so that the long term well being of the consumers and the society is taken ‘ care of. Thus, the societal marketing concept is the extension of the ’ marketing concept as supplemented by the concern for the longer term welfare of the society. Apart front the customer satisfaction, it pays attention to the social, ethical and ecological aspects of marketing.
Question 4.
List the characterstics of convenience products.
Answer:
The consumer products which a consumer usually purchases frequently, immediately and with minimum effort are called as convenience products. For example bathing soap, toothpaste, Bread, newspaper, cigarette, matchbox, medicine, cold drinks, grocercy items Convenience products oftenly are for immediate consumption. These are bought frequently and the consumer habits play an effective role in buying of convenience products. These products have the following features. ,
(i) These are less priced product.
(ii) These products are consumable or not durable products and cannot be stored for a long period.
(iii) Demand for these products is subject to daily needs, habits and consumer behaviour.
(iv) The buyers buy these product from the nearby shop.
(v) These products are easily available and thus take less shopping time.
(vi) These products are purchase frequently in small quantities according to daily needs.
(vii) Buyer generally knows the price of the product.
(viii) These products are not affected by fashion and style.
(ix) These products have no brand preference except those products which are demanded because of habit i.e. cigarette etc.
(x) Mass distribution policy is followed. Such products are available at every possible sales outlet.
(xi) Because of easy availability and close competition the price
of convenience products remain stable and low. ‘
(xi) The advertising and sale promotion activities are performed by the manufacturer.
![]()
Question 5.
Enlist the advntages of packaging of a consumer product.
Answer:
Consumer packaging : A consumer package is one which holds the required volume of a product needed for ultimate consumption and is within the means of a buying household. It is the package.in which the consumer actually gets the products.
Consumer packages are available in different sizes i.e. small, medium and large. The consumer has the option to purchase the pack size that suits his family size and budget. For examle package of tooth pastes, hair oils, soups, shampoo, face cream etc. Consumer packaging must be handy and attractive. – ‘ ”
Advantages of Packaging Packaging is beneficial for manufacturer, middlemen and consumer in the following manners.
1. Advantages of Packaging to the manufactures.
(i) Keep the product safe
(ii) Facilitates storage .
(iii) Enhances goodwill
(iv) Promotes product
(v) Prevents adulteration
(vi) Helpful in advertising and sales promotion
(vii) Facilitates distribution
(viii) Increases profit.
2. Advantages of packaging to the middlemen
(i) Facilitates storage .
(ii) Self advertising
(iii) Easy display
(iv) Helps in transmit
(v) Facilitate retailer’s function
(vi) Helpful in increasing sale and profit.
3. Advantages of packaging to the consumers
(i) Minimum possibility of adulteration .
(ii) Convenient handling and storage
(iii) Provides necessary information about the product
(iv) Helps memory and recognition
(v) Protects the contents
(vi) Payment of appropriate price.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the limitations of a advertising as a promotional tool? Enlist.
Answer:Limitations of Advertising
(i) Less forceful Advertising is an impersonal form of communication. It is less forceful than the personnal selling as there is no complusion on the prospects to pay attention to the message.
(ii) Lack of feed back The evaluation of the effectiveness of advertising message is very difficult as there is no immediate and accurate feed back mechanism of the message that is delivered.
(iii) Inflexibility Advertising is less flexible as the message is standardised and is not tailor made to the requirements of the different customer groups.
(iv) Low Effectiveness : As the volume of advertisement is getting more and more expanded it is becoming difficult to make advertising messages heard by the target prospects. This is affecting the effectiveness of advertising.
Question 7.
List five shopping products purchased by you or your family during the last few months,
Answer:
Shopping products : Shopping products are those products which are purchased by the customers only after comparing their quality, price, style, suitability etc. The customers of these products collect information of the price, shops, design, quality, utility etc. from different stores before the actual purchase. That is why these products are called as bargain products. Furniture, readymade garments, sarees, dress materials, shoes etc. are some examples. –
Features
(i) These products are available in good variety. They exhibit a high degree of differentiation.
(ii) Unit price of these products are higher that the convenience products.
(iii) These products are durable in nature.
(iv) These products are consumed slowly, so they are purchased less frequently.
(v) Shopping products are generally purchased occasionally by
the consumers. Such as Birthday, Wedding day, Diwali, New Year etc. .
(vi) These products are more complex, so consumer take more time in deciding what to purchase.
(vii) Consumers usually like to visit different stores or shopping centres before making their purchase.
(viii) Such products are influenced by fashion and style.
(ix) Mass distribution arrangement are not necessary since customers are not happy in deciding what to buy.
(x) Advertising and sales promotion activities are conducted by manufactures and middlemen both.
(xi) Rural buyer are generally interested to purchase such product from the nearby city.
(xii) Brand name, fashion and style, packaging store reputation, display and demonstration play an important role in boosting the sale of shopping products.
![]()
Shopping products are both homogeneous and heterogenous. Homogeneous shopping products are shoes, kitchenware, cosmetics, cookery, readymade garments etc. The price is an important factor for purchase of homogeneous shopping products.
Quality and style are relative!ytmore important factor for purchasing homogeneous shopping products like furniture, textile, household goods etc. These are the features of shopping products which a marketer must understand for framing a successful marketing strategy.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is marketing? What functions does it play with process of exchange of goods and services? Explain.
Answer:
Marketing includes all those activities, which are related to purchase and sale of goods and service. Business activities are not complete without marketing. Main functions are associated with management and marketing is most important among them.
Initially marketing implied purchase and sale of goods and services. However, at present it includes all those activities undertaken before and after purchase and sale of goods and services. In modern times, marketing includes consumer research, advertisement, sale policy and services rendered to consumers after the sale of goods and services.
Every institution undertakes work of two types
1. Production of goods and services.
2. Marketing of goods and services.
Both these functions are included in marketing. In this connection. Harry Hepner is of the view, “All those activities are included in marketing which help the goods to reach consumers from producers.” These include advertisement policies, price-determination, production planning and market analysis on the basis of customer to be found in future.
Definitions of Marketing
The definitions of the term ‘Marketing’ is classified in two categories for convenient study. These are
1. Definition in old, narrow sense or product oriented definition.
2. Definition in new broad sense or customer oriented definition.
1. Old, narrow sense or product-oriented definitions : These definition include most ancient, narrow physical distribution
of commodities and their production related activities.
(i) According to Tousley, Clark and Clark, “Marketing consists of those efforts which effect transfers in the ownership of goods and services which provide for physical distribution.” This definition include the transfer of ownership and physical distribution in the meaning of marketing.
(ii) According to Pyle
“Marketing comprises both buying and selling activities.” This definition of marketing consists only of the purchase and sale. It ignores the function of physical distribution and auxilliaiy function of marketing.
![]()
(iii) According to America Marketing Association Definition committee, “Marketing is the performance of business activities that direct the flow of goods and services from producer-to consumer or users.” This definition is an important over the earlier two definitions. It includes all the business activities relating to the production and d istribution of goods and services to the consumer or user.
Functional Activities
It includes the following functions
1. Market Research According to W.J. Stanton, “Marketing research is the systematic search for and analysis of facts related to a marketing problem. Its emphasis in shifting from fact finding information rathering activity to a problem solving and action recommending function.” Marketing research help in analysing the buyers’ habits, relative popularity of product, effectiveness of advertisement, media etc. Its major task is to provide the marketing manager with timely and accurate information so that better decisions can be made. The scope of marketing research is very wide. It may cover all the areas of business which have a bearing on the marketing function.
2. Product Planning Product: Planning is a process in which the form and design of product is determined on the basis of the facts obtained with the help of market research and then to make arrangement for the production of that product as per requirement. It is also an important function of the marketing nfanager. ,
3. Branding : A brand may be a name, a symbol, a sign, a picture or even the initials of the company’s name. The main aim of branding is to identify-distinctly the product of the company from similar products of the-competitors. It enables the consumers to differentiate the product of similar types and to make their choice of goods from among the various brands. The brand ensures the quality and standard of the product. It help a company in creating an image for its product in the market.
4. Purchase : Purchase is one of the important function of marketing. It is the first step in the process of marketing. A manufacture is required to buy raw materials for production purpose. Similarly, a whole-saler has to buy goods to sell them to a retailer. A retailer who has a direct link with the consumer has’also to buy goods to be sold to the latter. Thus, in all functions of exchange one aspect is purchase.
5. Standardising and Grading : Standardising and grading are the two very important aspects of present day marketing because with the help of these two aspects, marketing functions become easy, production becomes uniform, price become equal and marketing becomes extensive.
Therefore nowadays, the goods are produced on the basis of definite standards as to the quality of product, size of product, colour of product, weight of product, price of product etc. Standardising and grading make it easy v for both the consumer and seller to achieve their individual objects. This is the reason why sale and purchase of most of the goods become very easy on the basis of standardisation and gradation.
6. StorageStorage becomes necessary under two conditions :
when production is seasonal but consumption is perennial and also when production is continuous but consumption is seasonal. In other words, storage involves holding any preserving of goods between the time of their production and the time of their use. It facilitates a steady Flow of commodities to market throughout the year.
![]()
7. Transportation The function of transportation is to convey commodities from where their utility is relatively low to places where it is higher. Concentration of natural resources at certain place makes it necessary for industries to concentrate there.
This geographical division of labour and its advantages are made possible with the help of transportation.
The pricipal economics basis for transportation is in enhancing the value of goods by the creation of place utility. Even in the case of simplest marketing mechanism, where the consumer buys directly from a local firm or a factory, transportation is involved and must be undertaken either by the buyer or the seller.
8. Packaging Packaging is concerned with formulating container or wrapper for the product. Its main objective is to provide convenience in handling, ensure freshness and quality and to preven. adulteration. It also help in distinguishing the product of the company from that of competitors.
9. Selling Selling is another important function which involves transfer of the title of goods to the buyers. Selling is important from the point of view of the seller, the consumer and the general public. Efficiency in selling is the most important factor that effects the existence of a firm. The prime objective (viz profit) of a business concern is sucessfully carries out through sale of goods.
10. Advertising Advertising has become an important function of marketing in the competitive world. It helps to spread the message about the product and thus promote its sale, it facilities creation of a non-personal link between the advertisor and the receivers of the message. The importance of advertising has increased in the modern era of large scale production and tough competition in the market.
11. Pricing Pricing is also an important function which is closely linked to selling. Price policy of the concern directly affects the profit element and therefore its successful functioning. In determining the price policy, several factors are to be born in mind such as, cost of the product, competitors, prices, marketing, policies, government policy or customary or convenient prices, etc.
12. Finance It is the most important function of marketing. These are various kinds of finance requires, short-term finance, medium-term finance, long-term finance etc. There are various source of marketing finance too. For example, commercial banks, cooperative credit societies, government agencies etc. No Firm can depend solely on its own capital. Every business service borrows those products which were widely available at an affordable price.
Thus, availability and affordabililty of the product were consideres to be the key to the success of a firm. Therefore, greater emphasis was placed on improving the production and distribution efficiency of the firms resources. Marketing finance is necessary for the performance of various marketing functions. A business firm needs capital to hold inventories and to meet expenses of buying and selling goods. It also requires finance to provide credit facility to its regular buyer as considerable sales are on credit.
![]()
13. Risk TakingMarketing of goods involves innumerable risks :due to theft, deterioration, accidents etc. The most important factor responsible for the risk is flutuation in prices. The other factor may be change in fashion, competition in the market, change in habit of the consumers, natural clamities, etc.
Question 2.
Distinguish between the product concept and production concept of marketing.
Answer:
Marketing Management Philosophies In order to achieve desired exchanged outcomes with target market it is important to decide what philosophy or thinking should guide the marketing efforts of an organisation. An understanding of the phi I osophy or the concept to be adopted is important as it determines the emphasis or the weightage to be put on different factors in achieving the organisation.
For example, whether the marketing efforts of an organisation will focus on the product-saydesigning its features etc. or on selling techniques or on customer’s needs or the social concerns. ‘ The concept or philosophy of marketing has evolved over a period of time, and is discussed as follows:
Product Concept
As a result of emphasis on production capacity during the earlier days, the position of supply increased over period of time. Mere availability and low price of the product could not ensure increased sale and as such the survival and growth of the firm. Thus, with the increase in the supply of the products, customers started looking for products which were superior in quality, performance and features.
Therefore the emphasis of the firm shifted from quantity of production to products. The focus of business activity changed to bringing continuous improvement in the quality, incorporating’ new features etc. Thus, product improvement new features etc. Thus, product improvement become the key to profit maximisation of a firm, under the concept of product orientation.
Production Concept
During the earlier days of industrial revolution, the ^demand for industrial goods started picking up but the number of producers were limited. As a result, the demand exceeded the supply. Selling was no problem, Anybody who could produce the goods was able to sell. The focus of business activities was, therefore, on production of goods. It was believed that profit could be maximised by producing at large scale, thereby reducing the average cost of production. It was also assumed that consumers would favour.
Question 3.
Product is a bundle futilities? Do you agree? Comment.
Answer:
Product is the most important variable in marketing; second only to consumers. “If the first command in marketing is known the customer, the second is known the product”. This statement proves the importance of product in marketing. Product is the central hub of all the marketing activities of an entreprise. It is the soul of all the marketing efforts of an enterprise.
![]()
No marketing activities, production or sales, advertisement or sales promotion, price determination or physical distribution, can be imagined without the existance of a product. Product is the soul of all our marketing activities. Without a product, marketing cannot be imagined.
If a business and industrial enterprise is a body, management is its heart and market is its blood, it » will have to be in active without soul, in the same way as all the resources of an enterprise remain inactive without product. All the marketing programmes, policies, and pricing strategies are prepared for the product. All the marketing efforts begin with product and end with the product.
A successful marketing manager is one who concentrates upon the qualities and characterstics of the product of his enterprise. He must make his best efforts to study the needs, wants, tastes and habit of his customers and convert these specifications into product. No enterprise can be successful in achieving its marketing objectives if its products are not in accordance with the needs and wants of its consumers.
Therefore, it is necessary for all the business and industrial enterprises that they must maintain quality of their product which may meet the needs and wants of their consumers. They should fix the price of their products which can be afforded by their consumers and they should make these goods and services available to their consumers at right time and at right place and right quantity.
Product is a tool in the hands of the management through which it gives life to all marketing programmes. So, the main responsibility of the management should to know the product well. Someone has said, “If the first commandment in marketing is to know their customer, the second is to know their product.” In short, the importance of the product can be judged from the following facts
(i) Product is the central point for all marketing activities Product is the pivot and all the marketing activities revolve around it., Marketing activities, selling, purchasing, advertisement distribution, j sale promotion are all useless unless there is a product. It is a basic tool by which profitability of the firm is bargained.
(ii) Product is the starting point of Planning No marketing programme will be prepared if there i%no product because planning for all marketing activities like distribution, price, sales promotion,
advertising etc. is done on the basis of the nature, quality and the demand of the product. Product policies decide the other policies.
(iii)Product is an end The main objectives of all marketing activities is to satisfy the customers. It is the philosophy of the modem marketing concept. Various policy decisious are techniques to provide the customers benefits, utilies, and satisfication through product. Thus product is an end (satisfication of customers) and the product, therefore, must insist on the quality, size etc. of the product so that it may satisfy the customer’s needs. .
Thus, it is clear that the product is a must for marketing activities. It is true that all marketing activities are done for the satisfaction of customer and the producers must know their customers and their needs. The product must contain the qualities which can satisfy the customers.
The product, on one hand satisfies the needs of consumers and provides on the other hand, employment to crores of people in the activities of production^ distribution and advertisement, sale promotion transportation, warehousing etc. In this way product is most important from the point of view of the sellers, consumers and the society.
Question 4.
What are industrial products? How are they different from consumer products? Explain.
Answer:
Industrial products
Industrial product are the products which are used in producing other goods or services. These goods are not directly used by consumers. Raw materials, machinery, electric meters etc. are examples of industrial products. American Marketing Association has defined industrial good as “industiral goods are goods which are destined to be sold primarily for use in producing other goods or rendering services they include equipments (installed and accessory), Component
parts, repair and operating supplies, raw materials and fabricating materials.” This definition makes it clear that industrial goods are meant for use in producing consumer goods. Some are the goods which have common features of consumer goods as well as industrial goods such as tyre, sugar, coal and water etc.
Tyres serve as industrial goods when sold to the manufactures of vehicles and as consumer goods when sold to the owner of private vehicles. The number of buyers of industral goods is very limited. The buyers of industrial goods purchase these [ goods in bulk quantity. Price is an important consideration in the mind 1 of industrial buyers. Industrial goods may further be divided into four v parts as under:-
(i) Production facilities and equipmentProduction facilities !. and equipment include the facilities and equipments which help in , the process of production, For example, factory building, plant, fixtures spare parts, office equipment etc. These goods do not become a part of the finished goods. Generally these products are of technical nature. The price size, design and utility are the main considerations in the , mind of buyers of these goods. As price per unit of product is high and buyers are limited, the sellers requires continuous efforts for the , sale of such product.
![]()
(ii) Production Materials Production Materials include ‘ following three types of product.
(a) Raw Materials Generally, raw materials are supplied by ‘ natural resources such as agriculture product, mines and forests etc. Most of the agricultural products are the raw materials which require further processing and after such processing they are converted into consumer goods. The examples of raw materials are natural rubber, cotton, sugarcane etc. The cost of raw materials consitutes a large part of the total cost of producing a product.
(b) Semi-finished goods Semi-finished goods are the good which are finished goods for one unit and raw and materials for another unit. It is supplied by one industrial unit to another, such as :- iron, steel, and leas etc. Generally, semi-finished goods are manufactured at a large-scale and are directly supplied to their users.
(c) Fabricating parts Fabricating goods are the goods which are manufactures by one industrial unit and used by another industrial unit, without any further processing in producing consumer goods.” The important difference between the fabricating goods and semi-finished goods its that the fabricating goods are used by another industrial unit as these are supplied by the former unit while semi¬finished goods are further processed by the receiving unit. Examples of fabricating parts are-speaker of T.V, cabinet of T.V., tyre and tyre tube, light, horn, plug etc. of scooter.
(iii) Production supplies Production supplies are the product : which are necessary for the operation of industrial units but do not become the part of finished goods. The examples of production supplies are coal, gas, fuel, electric power, diesal, nuts, bolts, cleaning materials and lubricating oil etc.
(iv) Management Products : Management goods are the materials which are used in the process of management and administration of an enterprise etc. These include stationary books, typewriter, Fax machine, computers, registers etc. These goods are meant for use in business and not for producing a product.
Difference Between Industrial Product And Consumer Product
There are importance difference in marketing the industrial products and marketing consumer products. The main difference are as under
(1) Demand The prime difference in the marketing of these two goods is in the nature of their demand. The demand of consumer goods is original while that of industrial goods is derived. The industry is to supply the goods according to the wants of actual consumers or users. It means that the demand of industrial products is derived from the demand of consumer product in which the industrial products may play an important part.
![]()
(2) Market expansion Number of customers for industrial goods is very limited in comparison to consumer goods.
(3) Customer Customers of industrial goods are industrialists and manufacturers, while the buyers of consumer goods are the limited consumers.
(4) Product analysis Buyers of industrial product are well versed. They go by the merits and demerits of the product. They make detailes analysis of the product before buying. Whereas buyer of consumer products are both aware of the merits and demerits of the product. They do not make detailed analysis of the product before buying.
(5) Nature of Sales In the sale of industrial goods the personal contact with buyers plays an important role, whereas advertising programme and sales promotion play an important role in the sale of consumer products.
Question 5.
Distinguish between convenience product and shopping product.
Answer:
Convenience Product
The consumer goods which a customer usually purchases frequently and wants immediately and with minimum of efforts are called convenience goods. This category includes a wide range of household product of low unit value like soap, ball pen, pencil, exercise book, thread, biscuits, toffee, salt, newspapers, drugs etc.
These are the goods which are required by consumers frequently and ‘ immediately. These goods are of non-durable nature. The purchase of these goods are dominated by the buying habit of consumers. Generally consumer want to purchase these goods from the nearest shop or store. Easy and quick availability of these goods are the main charaeterstics Kof purchase of these goods.
Shopping Products
Shopping product are the goods, which the consumers select and buy after making comparision of substitutes on such criteria as suitability, quality, price and style. In case of a shopping product, a substantial number of consumers habitually make shopping comparision before they take a buying decision.
Woolens, furniture items, dress materials, shoes, sarees and jewellery arethe example of shopping goods. A shopping item is durable and is used up slowly.The consumers has to compare different manufacture offering and devote considerable time and effort to take buying decision. Generally in big cities there are specific markets for these product, such as Karol Bagh, Chandni Chowk, Cannaught Place in Delhi and Railway Road in Rohtak.
The marketing problem of the manufactures of such type of product are different from the convenience products. The institutions selling such products usually are large size and they buy the product in bulk quantity. The manufactures of such product usually deliver their product directly to the retailers of a large size. The marketing manager should emphasise on the advertisement and sales promotion programmes of such product in the nature that can reveal their superiority before consumers over other products in the market.
Question 6.
“Product is a mixture of tangible and intangible attributes”. Discuss.
Answer:
A product is anything which is bought and sold in the market. Various authors define the term ‘product’ in the following manner According to W. Alderson, ” A product is a bundle of utilities consisting of various features and accompanying services.”
According to Philip Kotler, ” A product is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquistion and consumptipn that might satisfy a want or need. It includes physical objects, services, persons, places, organisations and ideas.”
According to William J. Stanton, “A jproduct is a set of tangible and intangible attributes, including packaging, colour, price, manufacturers and retailers prestige and services, which the buyer may accept as offering satisfaction of wants and needs.”
According to Rustam S. Davar, “A product may be regarded from the marketing viewpoint as a bundle of benefits which are being offered to consumer”.
From the above definitions it is clear that anything that possesses utility is described as product. A product is both what a seller has to sell and what a buyer has to buy. Buyer will buy a product which can offer him expected satisfaction. In other words what a buyer buys is a mixture of expected physical and psychological satisfaction.
Thus, the term product does not mean only the physical product but the total product including brand, package, label, status of manufacturer and seller and the service offered to the customer. Prof. Philip Kotler has given an elaborated definition of the product including in it the services, persons, places, organisation and ideas.
Characteristics Or Essential Features Of Product
From the meaning and definitions of product, we can draw the following essential features of a product:
(i) Tangible attributes The first important feature of product is its tangibility. It means that it can be touched, seen and its physical presence felt. It is made up of glass, wood, metal etc. in a particular shape, size, colour, design, weight, length, taste,.fragrance, etc. for example, cycle, fridge, T.V. bread, bulb, etc.
(ii) Intangible attributes The product may be intangible in the form of service, such as banking, insurance, transportation, warehousing, etc.
(iii) Associated attributes From the marketing point of view the product should have some associated attributes such as brand name, package, warranty, etc. These attributes are helpful in differentiating the product of different manufacturers and create a distinct image of the product in the mind of the consumer, for example – LG, BPL, Philips, Sony, etc.
![]()
(iv) Exchange Value Whether the product is tangible and intangible it should have exchange value and should be capable of being exchanged between the buyer and seller for a mutually agreed price.
(v) Customer satisfaction Product should have the ability to offer value satisfaction to the consumer. The satisfaction may be both real and psychological, for example, when we buy Kwality Icecream, we also buy taste and flavour. ’
(vi) Satisfaction of business needs The last but also equally important feature of a product is that it’should also satisfy the business. From these essential features of a product it is clear that product may be a physical product or a service. From the marketing point of view, a product is bundle of expectation and benefits which are being offered to the consumers.
Question 7.
Describe the function of labelling in the marketing of products.
Answer:
A simple looking but important task in the marketing of goods relates to designing the label to be put on the package. The label may vary from a, simple tag attached to the product (such as in case of local unbranded products like sugar, wheat, pulses, etc.) indicating some information about the quality or price, to complex graphics that are part of the package, like the ones on branded products (say the graphic of boat and patwar on the pack of old spice, after shave lotion or of a lady offering a pen to solicit the views of the users, on the label of surf-excelnatic, a detergent powder manufactured by
Hindustan Lever Ltd). Labels are useful in providing detailed information about the product, -its contents, method of use, etc. What functions are performed by a Label? Let us look at some of the labels. The label on the package of a local tea company describes the company.
’Mohini Tea Company, Kanpur, an ISO 9001 : 2006 certified company. Dermicool Prickly heat powder, describes how the product provide relief from prickly heat and control growth and infection, giving caution forbidding its application on cuts and wounds. Pack of Maggie noodles describes the procedure of cooking noodles.
The package of Pepsodent list The ‘Ten Teeth and Gum problems’, which the product fights’with its ‘Complete Germicheck formula; Dabur Vatika enriched coconut oil describes the product as pure coconut oil with heena, amla, lemon and specifies how these are good for hair. Thus, one of the most important function of labels is to describe the product, its usage, caution in use, etc. and specify its contents.
The other important function performed by labels is to help in identifing the product or brand. For example, the name Parle Monaco imprinted on the pack help us to identify from numbers of packs which one is Parle’s Monaco biscuit. Also the common identification information provided by most lables is of manufacturer, net weight when packed, manufacturing date, maximum retail price and batch number.
The third function performed by labels is to help grading the products into different categories. Sometimes Marketers assign different grades to indicate different features or quality of the product. For example, Garpier hair conditioner comes in different categores for different hair, say for ‘normal hair’ and for other categories. Hindustan lever sells different types of tea under yellow, red and green label categories.
The fourth important function of label is to aid in promotion of the product. A carefully designed label can attract attention and give reason to’purchase. We see many product labels providing promotional messages,ibr example, the pack of Dabur Amla hair oil states, “Baalon mein dum, life mein fun”.
The label on surf excelmatic says, “Keep cloth look good and your machine in to conditions”. Labels play important role in sales promotional schemes launched by companies for exmple the label on pack of Dettol shaving cream mentions in different colours “40% extra free” or pack of Colgate toothpaste mentioning, “Free Toothbrush Inside”, or “Save Rs 15”.
Lastly, labelling performs the function of providing information required by law. For example, the statutory warning on the package of cigarette or pan masala, “Smoking is injurious to health” or “ChewingTobacco is injurious to health”. Such information is required on processed foods, drugs and tobacco products. In case of hazardous or poisonous material, appropriate safety-warning need to be put on the label.
![]()
Question 8.
Discus the role of intermediaries in the distribution of consumer non-durable products.
Answer:
Before analysing the functions and importance of middlemen or intermediaries in the distribution of products and services of non¬durable nature, it is pertinent to define in brief the meaning of non¬durable products and services and middlemen or intermediaries which may be defined as under :-
Non-Durable Products
According to America Marketing Association (AMA), “Non¬durable products are those products which can be used for one time or a few times.”
Non-durable products are tangible products that are normally consumed with one or a few uses. Non-durable products are divided into two parts :-
(i) One time use products;
(ii) A few time use products.
One time use products
These are generally perishable products, which can be used for only one time, for the direct satisfaction of human wants. Such as, Milk, Butter, Ghee, Vegetables, Fruits, Sweets:, Chocolates, Cigarettes, other eatables etc. The price of such products is normal. The are generally convenience products.
Demand for these products depend upon daily needs and habits of the consumers. There is less brand preference. These products are easily available in every market areas. Consumers demand these products according to their daily needs. These products are mostly purchased very frequently.
A few time use products
These are consumable products, which are consumed after a few uses. For example, Bathing soap, Washing soap, Refills, Toothpaste, Shaving cream, Shoe polish, Cosmetic items etc. If customer is satisfied there are more chances for repeat purchases. Advertising is the best way to promote these products. Heavy promotional expenses are needed for these products with a view to build up preference and loyalty among the customers.
Mass distribution policy is adopted for these products and these products are available at most of the shops with small profit margin. The marketing strategy for durable and non-durable products are quite different. Durable products need specific marketing through authorised dealership. The sales promotion activities are performed by the manufacturers and dealers both.These products have regular demand. This classification is also important for deciding the marketing strategy.
Services’
These are activities or benefits that provide satisfaction to the consumers. They cannot be stored and as such are perishable in nature. Its sales depend on quality as well as goodwill of the service provider, e.g. Services of Banks, Insurance Companies, Financial Institutions, Consultants, Chartered Accountants, Health Clubs, Fitness centres, Repair shops etc.
Meaning of Marketing Middlemen
Marketing middlemen or intermediaries are the persons or the organisations who provide a link between the manufacturers and the consumers. They facilitate the purchase and sales of goods and services and also perform the marketing functions such as buying and assembling, selling, packaging, financing, warehousing, transportation, advertising, risk taking, consumer research, after sale services, etc.
Marketing middlemen play an important role in marketing the products. In the distribution channel, there are manufactures and consumers, and in between them there.are some middlemen – wholesalers and retailers. In our marketing point of view the middlemen and intermediaries are the same.
![]()
The advertising agencies, warehouses, insurance companies, banks etc. facilitating functions in marketing, but cannot be called middlemen. Middlemen perform the marketing functions more economically than the manufacturers, at a given cost. Their specialisation and experience, offer to the manufacturer more than that what manufacturer can achieve at his own. Hence, marketing middlemen are intermediaries in between the producer and the consumer.
Definitions of Middlemen
1. “Middleman is one who specialises in performing operations or rendering services that are directly involved in the purchase and sale of goods in the process of their flow from producer to final buyer.” – American Marketing Association
2. “Middleman is an independent business concern situated in marketing channels at points between producer and consumers.” – Bechman
From the above definitions it is clear that, marketing middlemen/ intermediaries are the individuals and the organisations that perform various functions to connect the producers with the end-users.
Functions of Marketing Middlemen
Wroe Alderson is of the opinion that the main objective before marketing middlemen is to match the demand and supply of each segment. For this purpose, marketing middlemen perform various functions. He explained the following functions

1. Boost large scale production : The wholesalers give bulk orders to the manufacturers, which ‘ boost the large-scale production.
2. Purchase of raw materials : Some middlemen collect the raw materials from their areas and sell the same to the manufacturers in bulk quantity. They also provide raw-materials on credit basis.
3. Price determination : Middlemen have close relation with the buyers. They know their spending power, so they are best judge for accurate price determination. Thus, they assist the manufacturers in determining the prices of their products.
4. Demand forecasting : They provide necessary information relating to the future demand on the basis of their experience and knowledge.
5. Warehousing facilities : The middlemen give bulk order to the manufacturer even prior to production. The manufacturer sends the goods to middlemen just when goods are manufactured. The manufacturer, thus, does not require collection of the products.
6. Financial assistance : They make advance payment to the manufacturer for the purchase of goods. They also provide short-term financial assistance to the manufacturers during season period.
7. Standardisation and grading : The middlemen does grading of the goods on the basis of size, shape and other product standards after purchase made from the manufacturer.
8. Transport facilities : The wholesalers buy goods in bulk quantity. They also have their own vehicles to carry the goods from producer to consumers.
9. Advertising function : The middlemen advertise the products on which they deal and its advantage goes to the manufacturer.
10. Launching of new product : The middlemen introduce the consumers with new products and distribute free samples.
![]()
Importance of Marketing Middlemen
The marketing middlemen constitute an important link in the channel of distribution. They help the marketers in selling their products and the consumers in getting the want-satisfying products. The production process has now become so complex that a manufacturer is not in a position to make a direct contact with the consumers. The manufacturer has therefore, required assistance from the middlemen for the delivery of goods to the consumers.
Middlemen made the distribution easy and smooth. Many organised markets are created by them. They create time, place and possession utility. Middlemen concentrate their efforts on marketing and distribution of products. Middlemen are the link between the manufacturer and the ultimate consumers.
They direct the flow of goods and services from producer to consumers. Large-scale prodution become possible and profitable because of marketing middlemen. They perform the important function of advertising and publicity. They are the demand creators and match the demand with the production. The marketing middlemen provide invaluable services towards manufacturers, consumers and the society as a whole.
Question 9.
Explain the factors determining choice of channels of distribution.
Answer:
Distribution channels are an important part of the marketing mix of any business concern. Selection of appropriate distribution channel is very important because several elements of the marketing mix like price mix and promotion mix are closely interrelated with and interdependent on the distributing mix.
A good number of distribution channels are available to the manufacturer for bringing his product to the ultimate consumers or industrial users. Out of alternative channels, it is essential to make a right choice of distribution channel. The choice of the appropriate channel of distribution is not a simple job.
The manufacturer or the marketer has to make decision regarding the choice of most suitable distribution channel at minimum cost and attaining the desired level of sales volume. There are various factors both objectives and subjectives, which govern channel choice and vary from company to company.
While selecting a distribution channel, the marketer should carefully consider the following factors : –
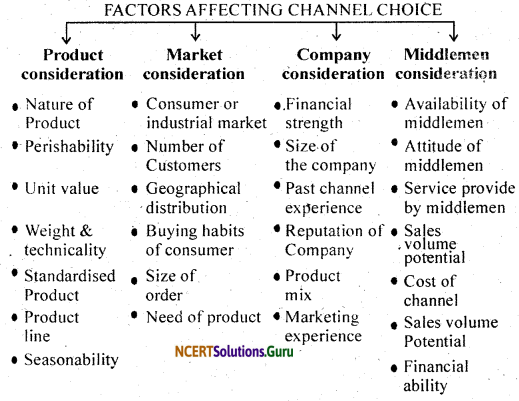
Question 10.
Explain briefly the components of physical distribution.
Answer:
Components of physical distribution – I Physical distribution management is that part of general management which is responsible for the design, administration and operation of the system to control the movement of raw materials and finished products. The structure of physical distribution is made up of ‘ following broad component namely
(i) Transportation
(ii) Warehousing
(iii) Inventory control
(iv) Material handling
(v) Order processing
The scope of Physical distribution is illustrated in the following diagram.
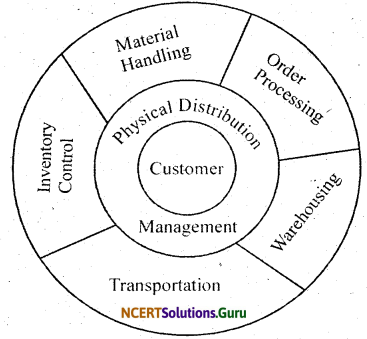
These components are dissimilar but they are all related to the common objective of maximisation of customer satisfaction and minimisation of costs. In order to achieve the various objectives and advantages of physical distribution various decision are to be taken by the management. These decision are known as physical distribution decisions.
![]()
Question 11.
Define advertising. What are its main features? Explain.
Answer:
Meaning of Advertising In marketing advertising is very important. No business can survive without advertising. So advertising is a must. The aim of every business is to earn profit and this aim can be achieved by selling goods at reasonable prices. The sales are possible only if the target audience knows about the availability of goods and they are persuaded to buy it. All this is possible through advertising which is deliberate action to popularise the product or service.
Thus advertising is commonly understood to communicate about a product or a service. But it is not correct and complete to understood so. Actually, advertising includes all the activities performed by an enterprise to present the goods and service to the consumers and to motivate them to buy these goods and services. In general term advertising is to announce publicity. Advertising is derived from a Latin word ‘adverto’. ‘ad’ means towards and ‘verto’ means turn. Thus, advertising means to turn attention towards a specific thing.
In other words, “Advertising consist of all the activities involved in presenting to a group, a non personal, oral or visual, openly sponsored message regarding a product or service or idea, this message called an advertisement, is disseminated through one or more media and is paid for by the identified sponsor”.
In this era of mass production and mass distribution where the firms land up with similar kinds of products, they face intense competition. To face competition, they need to widely publicise their product and try to portray their products as superior to’that of the competitors. And this is possible through advertising.
Definitions
(i) According to Americal Marketing Association “Advertising has been degined as ‘any paid form of non-personal presentation and promotion of goods, service or ideas by an identified sponsor.”
(ii) According to Mason and Rath “Advertising is a salesmanship without a personal salesman.”
(iii) According to Dr. Jones “Advertising is a sort of machine- made mass production method of selling which supplements the voice ‘ and personality of the individual salesman.”
(iv) According to Dr. Burden “Advertising includes those activities by which visual or oral messages are addressed to the public . for the purpose of informing them and influencing them either to buy any merchandise or to act to be indined favourably towards ideas, institutions or persons featured.”
(v) According to Sheldon “Advertising is a business force, which through the printed words, sells or help sale, builds reputations and fasters goodwill”.
(vi) According to Frank Presbrey : “Advertising is printed, written spoken or graphic salesmanship. Advertisement are designed to sell the products of the advertiser and to influence favourably the public mind individually and collectively – with respect to the interest of the advertiser.”
An analytical study of the above definition makes it clear that advertising includes all the activities through which a written or oral or visual messages regarding a product or a service or idea may be communicated to the people so that they may be persuaded to buy that product or service or idea. Thus, advertising means spreading of information.
Features of Advertising :-
On the basis of above definitions, the main characteristics or nature of advertising are an under
(i) Mass Communication : It is a unique means of mass communication announcing the sale of goods or services. It can help to introduce a new product quickly. Thus if any manufacturer request for purchase of a product at a time to only one or two customers, it cannot be said as advertising. However, it will be called advertising if uniform information is accessed to a number of persons at the sa’me time.
(ii) Non-Personal Presentation The advertising is a non¬personal salesmanship performing similar function like personal salesmanship. It is silent but forceful non-personal salesmanship.
(iii) Informative Advertisements are informative and provide valuable informations to the customers. These informations are in the form of information regarding the new product, regarding the characteristics of product and regarding the manner of use, etc.
(iv) Buying motive An advertisement inspires the consumers for purchase of a product., it lures the consumers for the purchase of the product by raising passion in their heart.
(v) Advertising expenses Money is incurred on advertising and such expenses are incurred by the person who is advertiser. The dissemination of information regarding service of the product, without such expenses, cannot be an advertisement.
(vi) Marketing toolAdvertising is a tool of marketing and it is a part of sales promotion.
(vii) Identified sponsor It is an openly sponsored sales message regarding and product or service i.e., the sponsor can be identified.
(vii) Commercial objects Commercial activities through advertising is made with an objective to increase the profit of an institution by enhancement of the sales of a product or service. All communication made with an additional objective to increase the sale by a commercial institution are left out of the limit of advertisement.
![]()
Question 12.
Describe the role of’sales promotion’ as an element of promotion mix. ‘
Answer:
“Selling” and “promotion” are often used synonymously selling has been degined as “the personal or impersonal process of assisting and/or persuading prospective customer to buy a commodity or a service Or to act favourably upon an idea that has commercial significance to the seller”.
Promotion is a broader term. It includes advertising personal selling, sales promotion and other selling tools. Promotion and sales promotion are different terms. Sale promotion is only a part of promotion. Promotion is a very wide term including advertising, personal selling, sales promotion and other promotional tools that can be devised to reach the goals of the sales programme.
The main purpose are to attract customers, awaken their demand and stimulate them to act in the desired manner. Sales promotion act as a bridge between advertising and personal selling to coordinate efforts in these two areas. The main tasks of promotional activities are to establish and maintain communication with large market segments.
Sales Promotion Sales promotion includes activities other than advertising, personal, selling, publicity and public relations which are used in promoting sales of the product or in persuading the customer to purchase the product. It serves as a bridge between personal selling and advertising. It is an aggresive method of selling.
According to American Marketing Association “Sales promotion includes the marketing activities other than personal selling, dealer effectiveness, such as displays shows and demonstrations, expositions and various current selling efforts, not in ordinary routine.”
It consists of short-term and temporary inantives to induce sales such as <i> Displays, <ii> Demonstration, <iii> sales contest, <iv> premium packs, <v> gift, <vi> exchange offer, <vii> coupons, <viii> off season discount, <ix> sampling, <x> exhibitions and fairs.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Marketing. How is it different from selling? Discuss.
Answer:
(i) New Broad or Customer-oriented concept of Marketing. The concept of Marketing lays more emphasis upon customers than production. Therefore, this concept is known as customer-oriented concepts. Main definitions of this concept are as follows.
(ii) According to Cundiff and Still, “Marketing is the business process by which products are matched with and through which transfers of ownership are effected.” This definition of marketing is clear that the producer produces goods and services, according to the needs and requirements of market or of Customers. Thus, it is clear that the functions of marketing commence well in advance before production. lliam J. Stanton, “Marketing is total system of interacting business activities designed to plan, price, promote and distribute want-satisfying products and services to present and potential customers.”
This definition, though very small in size, is perhaps the widest definition of marketing. It means that the function of marketing is to produce new and improved goods and service and to create the demand for these goods and services so that the standard of living of the society may be improved or the standard of living, once achieved by the society many be maintained.
(iii) According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing is the analysing organising, planning and controlling of the firms’s customer impinging resources, policies and activities wih a view to satisfy the needs and wants of chosen customer groups at a profit.
This definition makes very clear that all the marketing activities cluster around the needs and wants of consumers. These activies start with the discovery of such needs and end with the satisfaction of these needs.
(iv) According to Prof. Malcolm McNair, “Marketing is the creation and delivery of standard of living.”
This definition, though very small in size is perhaps the widest definition of marketing. It means that the function of marketing is to produce new and improved goods and services and to create the demand for these goods and services so that the standard of living of the society may be improved or the standard of living, once achieved by the society may be maintained.
![]()
(v) According to Institute of Marketing of U.K., “Marketing is the creative management which promotes direct employment by assessing consumer needs and initiating research to develop them. It co-ordinates the resources of production and distribution of goods services.
It determines and directs the nature and scale of the total efforts required to sell at maximum profitability the production to the ultimate users.” This definitions explains all the activities of marketing in quite detail. This definition also stremes upon the satisfaction of needs and wants of consumers.
(vi) According to Prof. H.L. Hansen, “Marketing is the process of discovering and translating consumer needs and wantsinto product and service specifications creates demand for these products and services and then in turn expanding this demand.”
This definition is considered to be a very important definition of marketing. It explains some very important fact of the meaning of marketing. First, Marketing function do not start with the production. They start well before production. First of all the needs and want of comsumers are discovered. Second, When the needs and wants of consumers are discovered, goods and services are produced to meet these wants and needs.
Third, demand is created for these goods and services and then this demand is expanded. Thus, this definition includes investigation regarding needs and taste of consumers planning for production of goods and services so that these needs may be effecively satisfied and the determination of marketing policies arid programmes.
(vii) According to E. Terome Me Charthy, “Marketing is the response of businessman to the needs to adjust production capabities to the requirements of consumer demands. This definition of marketing it clear that marketing is an activity of producing the goods and services to meet the demands of consumers. Thus, this definition also emphasises upon the demand and choice of consumer.
Conclusion
Thus modern marketing begins with the customer not with production cost, sales, technological landmarks and it ends with the customer satisfaction and social well-being. Under the market-driven economy buyer or customer is the boss.
Marketing is a total system of business, an on going process of
(1) Discovering and translating consumer needs and desires into t products and services (through planning and producing the planned products).
(2) Creating demand for these products and services (through \ promotion and pricing)
(3) Serving the consumer demand (through planned physical distribution) with the help of marketing channels, and then.
(4) Expanding the market even in the pact of keen competition.
The modern marketer is called upon to set the face of keen competition. The modern marketer is called upon to set the marketing objectives, develop the marketing plan, organise the marketing function, implement the marketing plan or programme (marketing mix) and control the marketing programme to ensure the accomplishment of the set marketing objectives. The marketing programme covers product planning or merchandising, promotion and physical distribution.
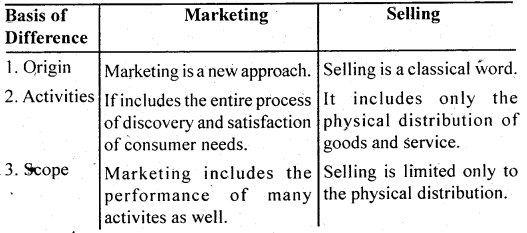
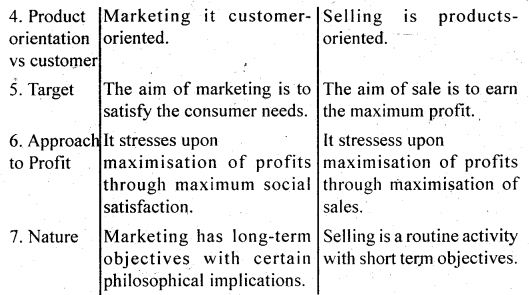
Difference Between Marketing and Selling . The words “Marketing” and “Selling” are often used as if they had the some meaning. It is however advisable to be clear as to the difference in meanings involved. Selling to normally concerned with the plans and ideas of trying to market the consumer exchange what he has (money) for what we have (i.e. goods or services).
Selling concentrates on sales, volume, whereas marketing is concerned with the needs of the buyer. Selling is preoccupied with the idea of satisfying a consumers requirements by means idea of the seller’s need to convert his product into cash. Marketing is concerned with the idea of satisfying a consumer’s requirementslbyjneans of the as well as by providing the customer with value-satfsfaction.
Difference between marketing and selling can be explained as under
![]()
Question 2.
What is the marketing concept? How does it help in the effective marketing of goods and services.
Answer:
Definitions of Marketing concept :-
Cundiff, Still, and Govani in their, Basic Marketing states that, “Marketing concept is a philosophy of management that strongly influences the management of marketing efforts in those companies . who adopt it.”
Philip Kolter in his book, ‘Marketing Management’ states that, “Marketing concept is customer oriented backed by integrated marketing aimed at generating customer satisfaction as the key to satisfying organisational goals.”
According to Arthus p. Felton, “Markeitng concept is a corporate , of mind that insists on the integration and co-ordination of all marketing functions, which in turn are welded with all the other corporate functions, for the basic objective of producing maximum long range corporate profit.
From the above definitions’ of marketing concept, we can conclude that “Marketing concept is a management that acts as a lamp-post for marketing activities, those are consumer oriented and stressed on the integration of marketing activities to earn adequate profit.”
New Concept of Marketing
The New Concept is consumer oriented. It considers consumer as the king around which all business activities rotates. It stresses on profit earning by providing the consumer with his desired products. Therefore, all the activities of the firm in the area of production, engineering finance and marketing of goods and services must be direction engineering, finance and marketing of goods and services must be directed primarily to determine what the consumer’s want and then satisfy these wants.
The consumer makes purchases. With certain expectations relating to price, quality, quantity and timely supply. A marketer who fails to identify these preferences fails to satisfy the consumer and as such he cannot run his business with success. Hence, all polices plans and programmes of the firm should be made so efficient that they might cater the need and wants of the consumers.
The new modern concept of marketing says that all business activities are integrated. Integration means composite functioning of all department of an organisation. Consumer satisfaction is the main stay of modern marketing concept. It realises that the business is a marketing organisation where all activities are directed towards the satisfaction of human wants. It believes it can win consumers loyalty and confidence by satisfying their wants. Modem concept totally accept the sovereignty of the consumer and.consider ‘Consumer is the King’.
The new concept of marketing can be illustrated as under
Definitions of new concept of Marketing

Modern authors view that, marketing is more than an physical process of distributing goods the services. They feel that marketing represents a distinct philosophy of business that has emerged over the recent years. The marketeers following this philosophy recognize and accept ‘customscriented’ way of doing the business. Different authors have given their definitions on new/modern concept of marketing.
According to Philip Kolter. “The marketing concept is a custome-oriented backed by integrated marketing aimed at generating customers satisfaction as the key to satifying organisational goals.” William J. Stanton, has defined the modern marketing as,
“In its fullest sense the marketing concept a philosophy of business which states that the consumers want satisfaction of the economic and social justification of a company’s existence. Consequently, all company’s activities in production, engineering and finance as well as in marketing must be devoted to first determining what the customer’swants and then, satisfying these wants still marking reasonable profits.”
The customer oriented idea of modern concept has been supported by many other authors also such as :
“Marketing is the creation and delivery of standard of living to the society.” – Malcom Me Nair
“Marketing is the managerial process by which products are matched with markets and through which transfers of ownership are affected. – Cundiff, Still and Govani
Significances of New Concept of Marketing:-
The adoption of New marketing concept is benefitted of for the business firm in the following ways
1. Helpful in product development:-Modern concept assumes : I consumer as a king of the market. Thus, the producer through its intensive market research try to identify the needs, wants and behaviour of the consumers and thus helps in discovery and development of new products.
2. More social satisfaction :- Under this concept only standard quality goods, are produced and are provided to the customer at reasonable price can easily be afforded by the consumers in sufficient quantity by them through the channel which is most suited to them and at the place and time of their choice. With the creation and delivery of standard of living, social satisfaction increases.
3. Positive impact on profitability The customer-oriented and co-ordinated approach to marketing has positive impact on the profitability of firm. It emphasised on earning profit through customes satisfaction.
![]()
4. Interaction with customers Modern Marketing concepts has both strategic and philosophical values. It assists the management in directing organisation efforts toward the long-term goals prolonged interation with customers also become possible.
5. Overall improvementOne of the important principles of modem marketing concept is co-ordinated and integrated marketing. The integrated marketing efforts are helpful in bringing overall improvement in marketing operations.
6. Useful in competitive market:- Attention towards customers needs is helpful for the management in spotting new products opportunities more quipkly. In a competitive market where existing products and brands are under constant attack by the competitors the development of new products is must. The best sources of new product idea is unsatisfied needs of the company’s customers.
7. Complete evaluation Modern marketing concept leads to follow on integrated and co-ordinated approach to marketing. By concentrating on consumer’s wants management can evaluate contributions made by the different departments of the firm in a better way.
8. Growth of the firm :- Modern marketing concepts has strategic implication as it allows the business firm to direct its activities towards broader and long range objectives. Like sustained interaction with the customers, and stability and growth of the firm.
Finally the interest of the company/firm and the interests of the society are harmonize. The management realises that its interest and the interests of the society are one and same and that the future profit of the company should come through the satisfaction and welfare of human want and needs.
Question 3.
What is marketing mix? What are its main elements? Explain.
Answer:
Meaning of Marketing mix
Marketing mix is the policy framework adopted by the marketeer to get success in the field, of marketing. It refers to the amounts and kinds offnarketing variables, the firm is using at a particular time. Under .marketing mix, we include product mix, promotion mix and distribution mix.
It is rightly remarked that it is not the product but the satisfaction ‘ that are sold now-a-days in order to be a successfull marketeer. One ‘must care for customer satisfaction. For this one should know the real need of his customer and then use the resources to purchase the products which will best satisfy the identified needs. A customer- oriented firm performs number of functions to satisfy customer needs.The effective coordination of these function is often called as marketing mix.
Definition of Marketing Mix
Marketing mix is the combination of the product, the distribution system, the price structure and the promotional activities. Different authors define the term marketing mix in the following manner :
According to R.S. Davar, “The policies adopted by the manufacturer to attain success in the market constitute the marketing
According to Me Carthy, “Marketing mix in the park of four sets of variables namely product, price, promotion and place variables. According to William J. Stanton, “Marketing mix is the term used to describe the combination of the four inputs which constitute , the core of a company’s marketing system – the product the price structure, the promotional activities and the distribution system.
Marketing mix is a term generally used to denote a particular combination of marketing variables which are controllable by an Sb enterprise and which are used to appeal a particular market segment.
Philip Kotler has defined it as, “the set of controllable variables that firm can use to influence the buyer’s responce.” Hence, the marketing mix can be regarded as the ‘core of the company’s marketing system.
Nature of Marketing Mix
Marketing mix is the instrument for the attainment of marketing goals. Marketing mix denotes a combination of various element which in their totality constitute firm’s marketing system. It should be noted that four ingredients, elements of marketing mix are interrelated because the decision takes in one area usually affects the other. The nature of marketing mix concept should be clean from the following explanation : .
I. Product Mix The product itself element. Product must satisfy consumer needs, product mix includes the physical product,- product services, branding, packaging, colouring, standardising, planning and developing right.
The product is the focus of all marketing activities.
![]()
Product is sum total of tansible and intansible attributes including, product design style-size, quality colour, brand name, packaging, labelling after, sales services etc. Production mix also include product differentiation, standardisation and grading, product lines etc. Hence, product mix is the total of allproduct, offered for sale by a company. Some important variables of product mix are explained here :

1. Product design Product design is a very important feature especially in consumer products like shoes, readymades garments furniture, crockeiy, automobily etc. Product should be designed in a manner as desired by the target consumers.
2. Product line Product line is a group of closely related products which are able to satisfy a similar class of need for example, BPL Co manufacturing Television, Refrigerators. Music System, Washing, Machines, etc.
3. Product quality Product quality depends on design, material used, manufacturing process, workmanship packaging etc. Generally, specific grade or standards of quality of the product are determined either by agreement among the producer or by law. The quality can be fixed interni of size weight colour, shape, appearance, flavour, finish, strength and other physical features depending upon the nature of the product.
(ii) Price Mix The second element which effect the volume of sale is the price mix includes determing pricing objective and policies prices. Fixation discount polity concession policy, profit margin, terms of payment, credit policy etc. Price of the value of a product expressed in terms of money.
It is a matter of vital importance to the buyes and the seller. Exchange of goods and services take place only when the price is. agreed upon between buyes and the seller. Price is the primary source of revenue to a firm. The success or failure of a firm depends upon its pricing policy. That is why every marketeer takes special interest in fixing and implementing his pricing, policy. The price mix of a firm include the following items :
Pricing objectives, pricing policies, prices determination, term of credit discount policy, concession policy, term of delivery, leve of margin, resale price maintenance.
(iii) Promotion Mix The third element of marketing mix persuade and attract the customers. Promotion is the persuasive communication about products of the company. Promotion mix includes : Personal selling, advertising sales, promotion activities public relations displayed and demonstrations participation in trade , fairs and exibitions etc.
(iv) Place Mix The fourth element creates time place and possession utilities. The place mix also known as distribution mix is the co/nbination of decisions relating to distribution channels storage facility location inventory level transportation warehousing etc.
These four elements of marketing mix are co-equal interdependent and essential. The decissions on the four elements of marketing mix must be properly coordinated and balanced in order to achieve an optimum marketing mix.
Elements of Marketing Mix
According to Neil H. Borden, Marketing mix consists a list of the important element or ingredients that make-up the marketing ; programme.”
Elements of marketing mix means composition of marketing mix. The marketing mix is dynamix in nature. It changes with the change in internal and external forces. Each marketing firm has its own unique marketing mix. Such inter-firm deviations arises due to the differences in their product policy price policy promotion policy and distribution 5 policy. Moreover different authors explain the elements of marketing mix in different ways.
1. Prof. Albert W. Frey in his book, “Advertising has explained the element of marketing mix using two dimenstons.
(i)Product related variables :- (i.e. offering) if include product, Brand Packages, Prices service etc.
(ii) Procedure related variables : (i.e. tools) it Includes, advertising distribution channel, personal selling promotion etc.
(iii) H.A. Lipson and J.R. Darling in their book, “Introduction to Marketing Adminstration has explained four types of element such as :-
- Product
- Condition of sales
- Distribution
- Communication
(iv) Jerome E. Me Casthy in his book “Basic Marketing explained four types of element of marketing mix in term of’four Ps’ because each element start with the English alphabets ‘p’. These are :- Product, Price, Place and Promotion. These four fold classification of marketing mix and are accepeted by many , scholars.
![]()
Question 4.
How does branding help in creating Product differentiation? Does it help in marketing of goods and services? Discuss.
Answer:
Before answering the importance of branding the meaning of branding is essential.
Branding One of the most important decisions that a marketer has to take in . the area of’product’ is in respect of branding. He has to decide whether the firm’s products will be marketed under a brand name or a generic name. Generic name refers to the name of the whole class o’ the product.
For example, a book, a wristwatch, tyre, camera, toilet soap, etc. If products were sold by generic names, it would be very difficult for the marketers to distinguish their products from that of their competitors.
Thus, most marketers give a name to their product, which helps in identifying and distinguishing their products from the competitor’s products. This process of giving a name or a sign or a symbol etc., to a product is called branding. The various terms relating to branding are as follows ’
(i) Brand A brand is a name, term, sign, symbol, design or some combination of them, used to identify the products – goods or services of one seller or group of sellers and to differentiate them from those of the competitors. For exmaple, some of the common brands are Bata, Lifebuoy, Dunlop, Hot Shot, and Parker. Brand is a comprehen sive term, which has two components – brand name and brand mark. For exmaple,-Asian Paints has the symbol of Gattu on its pack, which is its brand mark. .
(ii) Brand NameThat part of a brand, which can be spoken, is called a brand name. In other works, brand name is the verbal component of a brand. For example, Asian paints, Saffola, Maggie, Lifebuoy, Dunlop, and Uncle Chips are the brand names.
(iii) Brand MarkThat part of a brand which can be recognised but which is not utterable is called brand mark. It appears in the form of a symbol, design, distinct colour, scheme or lettering. For example, the Gattu of Asian paints or devil of Onida or symbol of Yogkshma of LIC, or four fingers and a palm of Anacin are all brand marks.
A very important decision area for marketing of most consumer products is whether to sell the product in its genric name (name of the category of the product, say Fan, pen, etc) or to sell them in a brand name (such as Polar Fan or Rottomac pen) Brand name helps in creating product differentiations i.e. providing basis for distinguishing the product of a firm with that of the competitor, which in turn, helps in building customer’s loyality and in promoting its sale.
The important decision areas in respect of branding include deciding the branding strategy, say whether each product will be ” given a separate brand name or the same brand name will be extended to all products of the company, say Phillips Bulbs, Tubes and Television or Videocon Washing Machine, Television, and Refrigerator. Selection of the brand name plays important role in the success of a product.
Advantages to the Marketers
(i) Enables marking product differentiation Branding helps a firm in distinguishing its product from that of its competitors. This enables the firm to secure and control the market for its products.
(ii) Helps in advertising and display programmes :-A brand aids a firm in its advertising and display programs. Without a brand name, the advertiser can only create awareness for the generic product and can never be sure of the sale for his product.
(iii) Differential Pricing Branding enables a firm to charge : different price for its products than that charged by its competitors. This is possible because if customers like a brand and become habitual 1 of it, they do pot mind paying a little higher for it;
(iv) Ease in introduction of new productIf a new product is introduced under a known brand, it enjoys the reflected glory of the brand and is likely to get off to an excellent start. Thus, many companies with established brand names decide to introduce new products in the same name. For example, Food Specialties Ltd. had a sucessful brand Maggie (noodles), It extended this name to many of its new products introduced such as Tomato Catch Up, Soups, etc. Similarly Samsung extended the brand name of its Television . to Washing Machines and other durable products, like Microwave oven.
Advantages to Customers
(i) Helps in product identification Branding helps the customers in identifying the products. For example, if a person is satisfied with a particular brand of a product, say tea leaves or detergent , soap, he need not make a close inspection every time he has to buy
that product. Thus, branding greatly facil itates repeat purchase of the products.
(ii) Ensures Quality Branding ensures a particular level of quality of the product. Thus, whenever there is any deviation in the quality, the customers can have recource to the manufacturer or the marketer. This builds up confidence of the customers and helps in increasing his level of satisfaction.
(iii) Status symbolSome brands become status symbols because of their quality. The consumers of those brands of products feel proud of using them and adds to the level of satisfaction of the customers.
Question 5.
What are the factors affecting determination of the price of a- product or service? Explain.
Answer:
The price of a product influences its wage, rent interest and the profit. It again influences the economic means. High wage attract the labourers and high rate of interest attarcts investment.
Promotion and advertisement of a product too depend on its price. If the product has the capacity to bear such expenses, these are incurred, otherwise the firm obstains from incurring it.
There are some laws for imposing restrictions on the prices in every country and these influence the price policies and the strategies, Other laws of similar nature are made for the distribution, advertisement, packaging etc. on account of these rules, no manufacturer reveals his price policy.
Therefore, pricing decisions play a very important role in the desing of the marketing mix. Pricing strategy determines the firm’s position in the market against its rivals. Price is a powerful marketing instrument. As a marketing weapon, pricing is the big-gun. However, it must be used with great caution as is dangerous and explosive market force. It may doom a good product to failure.
Therefore, all marketing managers must make accurate and planned pricing decisions.
Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions
The pricing decisions are influenced by many factors. The price policies should be consistant with pricing objectives. The influencing factors for a price decision can be divided into two groups.
(1) Internal factors and
(2) External factors.
1. Internal Factors
(i) Organisational factor’s Princing decisions occur on two levels in the orgnisational overall price strategy is dealt with by top executives. They determine the basic rates that the product falls into in terms of market segments. The actual mechanics of pricing are dealt with at lower levels in the firm and focus on individual product strategies, Usually, some combination of production and marketing , specialists are involved in choosing the price. –
(ii) Marketing Mix : Price is the one of the important elements of the marketing mix. Marketing experts view price as only one of the many important elements of marketing mix. A shift is any of the elements has an immediate effect on the other three-production, promotionand N distribution. In some industries, a firm may use price reduction as a marketing technique, others firms may raise.
prices as a deliberate strategy to built a high – prestige product line. In other case, the effort will not succed unless the price change is combined with a total ’ marketing stratgey that supports. A firm that raises its prices may add a more impressive looking package and may begin a new advertising compaign.
(iii) Product Differentiation Generally, the more differentiated a product is from competitive products, the more leeway the Firm has in setting prices. When a Firm’s Product is basically the same as that of its competitors, the firm can differentiate its own image by building a solid reputation among customers, by charging different prices.
(iv) Objectives of the enterprise Objectives of the enterprise affect pricing decisions to a significant extent. There may be many objects of the business and industrial enterprises. Some important objects of a business and industrial enterprises may be to earn proper return on investment, to earn maximum profits through maximum sales, to bring price stability, to bring stability in the margin of profit, to face the competition, to increase market share or to maintain it, to determine the prices of products according to the paying capacity of consumers and long-term welfare of the enterprise.
![]()
(v) Cost factors Cost factors are the most important factors affecting pricing decision of an enterprise. Cost factors include the following,
- Cost of. raw materials
- Manufacturing cost,
- Administrative overheads
- Cost of transportation
- Cost of storage
- Cost of advertisement
- Cost of distribution, and
- Cost of Selling etc.
2. External Factors
These are the factors over which the firm has no control, and therefore marketers have to face many difficulties while determining the price of a product. Such factors are
(i) Demand It has a large impact on pricing since demand is affected by such factors as the number and size of competitors, what they are charging for similar products, the prospective buyers, their capacity and willingness to pay, and their preference, these factors need be taken into consideration while fixing the price.
(ii) Competition : The knowledge of what price the competitors are charging for similar product and what possibilities lie for raising or lowering prices also affect pricing.
(iii) Suppliers of Raw Materials Suppliers of raw materials and other articles can have a significant role on the price of a product. The price of a finished product is directly linked with the price of the Raw Material etc. Hence, if the suppliers raise the price, the ultimate result is a raise in price by the manufacturer, who ultimately passes it on to consumers. Scarcity or abundance of the raw materials also affects pricing.
(iv) Channels of Distribution of the product If a product passes through many channels of distribution from producer to consumers, the price of such product will be higher because every channel of distribution has to be paid some remuneration will have to be paid to its channels of distribution.
(v) Economic conditions The inflationary or deflationary tendency affects pricing. In recession period, the prices are reduced to a sizeable extent to maintain the level of turnover. On the other hand, the prices are increased in boom period to cover the increasing cost of production and distribution. To meet the changes in demand, prices etc. several pricing decisions are available
- Prices can be boosted to protect profits against rising cost
- Prices protection systems can be developed to link the price on delivery to current costs
- Emphasis can be shifted from sales volume to profit margin and cost reduction etc.
(vi) Buyers The various consumers and businesses that buy a company’s products or services may have on influence in the pricing decision. Their nature and behaviour for the purchase of a particular product, brand or service etc. affect pricing whom their number is large.
(vii) Pricing policies of competitors Pricing policies of competitors of a product also play an important role in the determination of price of the product. If the price determined by the competitors for their product is low, the enterprise will also have to keep its price low.
(viii) Trade conditions and customs Prevailing conditions and customs in marketing a particular product also affect pricing decisions of an enterprise. For example, guarantee of free service for a certain period has been a common practive for consumer products of technical nature, such asT.V., Refrigerator and Tape-Recorder etc. Therefore, the price of such products must be determined keeping in view the estimated cost of repair of these products for such period.
(ix) Government Regulations Price discretion is also affected by the price – control by the government through enactment of legislation, when it is throught proper to arrest the inflationary trend in prices of certain products. The prices cannot be fixed higher, as government keeps a close watch on pricing in the private sector.
![]()
Question 6
What do you mean by ‘Channels of distribution’? What functions do they play in the distribution of the goods and services? Explain.
Answer:
It is not enough to produce the goods and services of best quality at minimum cost, it is equally important, rather more important that these goods and services must be made available to the consumers at proper time and at proper places because ultimate object of every manufacturer is to earn maximum profit through maximum sales and the object can be achieved only if the goods and services are rightly distributed to their consumers. Goods and services may be distributed to the consumers through different ways. The ways through which the goods and services are distributed from manufacturer to the consumers, are called channel of distribution.
Definitions
(i) According to Philip Kotler”Every producer seeks to link together the set of marketing intermediaries that best fulfil the firm’s objectives. This set of Economic intermediatories is called the marketing channel.”
(ii) According to William J. Stanton “A channel of distribution for a product is the route taken by the title of the goods as they move from the producer to the ultimate consumers or Industrial user.”
(iii) According to Me Carthy “Any sequence of Institutions from the producer to the consumer including none or any number of middlemen is called a channel of distribution.”
On the-basis of analytical study of above definations it can be concluded that a channel of distribution is a chain through which a producer transfers the ownership of his goods and services to his consumers. Channels of distribution are also knwon as middlemen, agents of distribution, and distribution chains. A channel of distribution is a bridge to cover the gap between a manufacturer and consumers.
Channels of Distribution.
In case of large number of consumer products, the potential buyers are scattered over wide geographical area. In order to contact these people efficiently and efficiently, it is important to take the help of number of intermediaries as contacting them directly may not be cost effective and may be difficult even otherwise for example, a manufacturer of detergent powder in Gujarat would find it very difficult to directly approach customers, say in Delhi, Thirvant purarn, Bhubneshwar, Hydrabad, Srinagar and other for off places.
Therefore, he/she would supply a %ti$e quantity of his/her product to a big merchant, say in Hydrabad this big merchant would then supply detergent power to relatively small sellers in various towns of Hydrabad. These sellers would in turn, resell the goods to consumerIn this manner, goods are distributed from the place of production to | the place of consumtion. These people, institutions merchants, and l functionaries, who take part in distribution function, are called L ‘Channels of distribution’.
Channels of distribution are set of firms and individuals that take title, or assist in transferring title to particular goods or services as it moves from the producers to the ponsumers. In other words, channel refers to a team of merchants, agents and business Institutions that i combine physical movement and title movement of products to reach ! specific destinations.
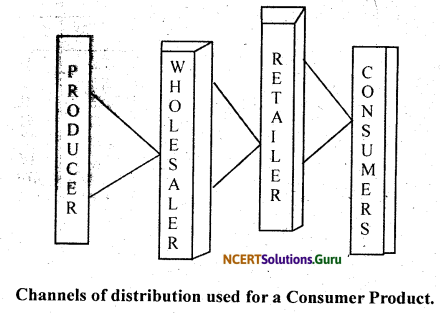
Mostly goods and servies are distributed through a network of marketing channels, for example we buy merchandise of our need such as salt,.bulb, tea, sugar, soap, paper, books, flour,.etc. from retail sellers.
The channels bring economy of effort. This can be better understood with the help of an example. Let us say you have to buy four things, viz, sugar, bulb, coffee and ink. Most probably you would walk into a general merchant’s shop and buy all the articles from one place. Imagine what would happen if there were no middlemen or general merchants available. In that case you would have to buy directly from the manufacturers of these products.
You will have to make four contacts, each with the producer of sugar, bulb, coffee and ink. Compared to this, there was only one contact when all the things were bought from the same general merchants. Now let us assume that there are four customers. Needing the same four articles. In all sixteen contact would have to be made. In case middleman are used, as shown in the part II of figure, only eight contacts could be needed. Thus, use of middleman brings economy of efforts.
![]()
A part from the economy of effots, middleman help to cover large geographical area and bring efficiency in distribution, including transportation, storage and negotiation. They bring convenience to customers as they make various items available at one store and also serve as authentic source of market information as they are in direct contact with the consumers.
Functions of Distribution Channels Channles of distribution smoothen the flow of goods by creating possession, place and time utilities. They facilitate movement of goods by overcoming various time, place and possession barriers that exits between the manufacturer and consumers. The important functions performed by middleman are as follows ,
(i) SortingMiddleman procure supplies of goods from a vairety of sources, which is often not of the some quality, nature, and size, for example, a wholesaler of cashew nuts may procure a large quantity from different cashew nut producing areas, which would contain nuts of varied quality and sizes. He/She then sorts the nuts into homogenous groups on the basis of the size or quality.
(ii) Accumulation This function involves accumulation of goods into larger homogeneous stocks, which help in maintaining continious flow of supply.
(iii) AllocationAllocation involves breaking homogenous stock & into smaller, marketable lots for example, once cashew nuts are graded . and large quantities ate built, these are divided into convenient packs of say 1 kg, 500 grams and 250 gms, to sell then to difffernent types of buyers.
(iv) Assorting Middleman build assortment of products for resale. There is usually a difference between the product lines made by the users, for example, a cricket player may need a bat, a ball, wicket, gloves, helmet, a T-shirt, and a pair of shoes.
(v) Product Promotion Mostly advertising and other sales promotion activities are organised by manufacturers.
(vi) Negotiation Channels operate with manufacturers on the other hand and customers on the other Arriving at deals that satisfy both the parties is another important function of the middleman.
(vii) Risk Taking In the process of distribution of goods the merchant middleman take title of the goods and thereby assume risks on account of price and demand fluctuations, spoilage, destruction,etc.
Question 7.
Explain the Major activities involves in the physical . distribution of Products.
Answer:
Physical distribution is the process of reaching the product i to the consumers it encompasses all the activities involved in the physical flow of products from producers to consumer. Physical * distribution creates ‘time’ and ‘place’ utility which maximize the value
of a product “by delivering them to the right customer at the right time and place”. In otherwords, its objectives is to “put the product . within an arm’s length of desire” Physical flow of – (a) Raw Materials
(b) Finished products from the points of origin to the point of use/consumption to meet the customer needs at a profit. Physical distribution may be defined as “a term employed in ‘ manufacturing and commerce to describe the broad range of activities.
Concerned with efficient movement of finished products from the end of production line to the consumer. Recently, physical distribution has been expanded into the broader concept of supply chain management. This modem concept is the heart of today’s market logistics systems.
Deflations
According to W.J. Stanton, “Physical distribution involves the management of the physical flow of products and the establishment and operation of flow system.” .
According to Me Carthy, “Physicdistribution is the actual handling and moving of goods within individual firm and along channel system”.
On the basis of analytical study of above definitions. It can be concluded that physical distribution of goods and services includes all the activities to be performed from the stage of production to the stage of consumers of these goods and services.
Activities of Functions Performed in Physical Distribution ‘ System
Physical distribution process involves co-ordination and integration of many managerial decisons.
(1) Size of Inventory
(2) Warehousing
(3) Transportation „
(4) Material Handling
(5) Size of the order
(6) Procedure to process the order
All six decisions areas are interrelated and interdependent. What is done in one area certainly affects decision-making in other related areas.
(1) Size of Inventory The very decision to be taken by Management of an enterprise in the Management of physical distribution of products is in regards to the size of Inventory.
(2) Warehousing The next decision regarding Physical distribution is the decision on ware housing location. The decision is closely related to the decision on inventroy size.
(3) Transportation :- Decision on modes of transportation largely depends upon the size’of inventories and the location of the storage, so that which are interrelated because economy in transportation charges may increae the storage cost or vice versa.
(4) Material Handling Handling of products is an important function to be performed in the process of management of physical distribution.
(5) Size of the order Size of order is one of the significant factors to be considered. While taking a decision in respect of packaging and means of transportation. Orders of less quantities will increase the cost of handling because the handling process will be done entirely by hand instead of machines.
![]()
(6) Procedure to process the order It is a very important for the management how tjre orders will -be processed. The management must arrange all the physical and human resources of the enterprise in such a manner that the orders received in the enterprise can be processed at the earliest because it increases the goodwill of the enterprise and if helps in increasing the sales of the enterprise.
Question 8.
‘Expenditure on advertising is a social waste’. Do you agree? Discuss.
Answer:
Though there are many advantages of advertising, it cannot be said that there is no disadvantage of advertising and that it is free from critical. The fact is that it has been strongly criticised by many eminent scholars because of many reasons. Some scholars have commented that, “Money spent on advertising is wasteful.
Some other scholars have commented. “Advertising leads to falsehood in Business.” In the light of such strong criticisms, it becomes necessary to analyse the reasons for which it is criticised, Important disadvantages of advertising may be explained as under .
(1) Increase in Price The expenses incurred on advertising are added to the sale price of the product it increases the price of a commodity unduly. Generally, manufactureres spend a lost of money on advertisement, which increase the cost of production.
(2) Increases in Consumer needs It just takes business from one concern and gives, it to another for example, people today are acquainted with the use of soap, paste, telcom powder.
(3) Advertising is not productiveIt is true that the advertising does not produce any tangible goods. But all productive work not necessarily results in tangible goods.
(4) Advertising forces people to desire and buy things which in fact are not with in their means ft is true that advertising arouses interest for buying. But there is no physical force exerted on customers to buy things. ‘
(5) Tendency of MonopolyAdvertising encourages monopoly because almost all the effective media of advertisement are too costly to be afforded by the manufacturers of large scale only which encourages monopoly.
(6) Use of obscene advertisementThe statement, pictures etc. in many cases are offensive, vulgar and immoral.
(7) Social evilCigarattes, biri, wine, etc. are harmful to health. Advertising makes people to buy these, ft affects their health.
(8) False advertisementThere is often superlative description or false description of the product in the advertisement. Every advertiser portrays his product as the best, e.g. ’Number one in India,’ ’Best Product’.
Money spent on Advertisement is not a Waste . It is often said that advertising is a waste. Advertisement increases cost and the money spent on advertisement is fruitless, as such it should be stopped. Advertising has proved its success and effectiveness in enhancing the consumtion and production. Some of the criticism above may be true but not absolutely correct. Following are the arguments advanced against above criticims.
(1) False advertisementMany advertisement; give superflows and false statements claiming their product to be the best. There is exaggeration of real facts. But such products are short lived. Such products soon go out of the market.
(2) Cost of advertising is not a burden upon consumers One of’the strong criticisms against advertising is that the cost of advertisement is added to the cost of production which increase the cost per unit and in this manner proves a burden upon
consumers. Increase in scale of production brings savings as it decreases per unit cost of production.
(3) It does not encourage monopoly Advertising is strongly criticised on the ground that it encourages monopoly but it is also not ture. It creates healthy competitive market for the products.
(4) No wastage of Natural and National resources Some of the critics of the advertising argue that it involves the wastage of natural and national resources. This argument cannot be regarded well as it supported the use of resources for right purpose.
(5) Social evils It is said that advertising is responsible for causing and creating many social evils but it is not absolutely true.
(6) It does not encourage the use of Luxuries The criticism that advertising encourages the use of luxuries is also not very true. The fact is that is makes the new products and their uses known to the consumers which helps in making their selections and in increasing their standard of living.
(7) It does not make the selection difficult Advertising is said to make the selection difficult but the fact is that it helps the consumers in making their selections because with the help of advertisement, consumers can decide what to purchase and from where to purchase.
Question 9.
Distinguish between advertising and personal selling.
Answer:
Advertising
“If you’re trying to persuade people to do something, or buy something it seems to me you should use their language, the language in which they think.” – David o gilvy
“We find that advertising works the way the grass grows, you can never see it but every week you have to mow the lawn”. – Andy Travis
We generally come across hundreds of advertising messages everyday, which tell us about various products such as toilet soaps, detergent powder, soft drinks and services such as hotels, insurance policies, etc. –
The important distinguishing features of advertising are as follows:-
(1) Paid form Advertising is a paid form of communication. That is, the sponsor has to bear the cost of communication with the prospects.
(2) Impersonality There is no direct face to face contact between the prospect and the adviser. It is therefore referred to as impersonal method of promotion.
(3) Identified sponsor Advertisement is undertaken by some Identified Individual or company, who makes the advertising efforts and also bears the cost of it.
Personal selling
“Most people think “Selling” is the same as “Talking”. But the most effective sales people know that listening is the most important part of their job.” -RoyBartell
You don’t close a sale, you open a relationship if you want to build a long term successful enterprise.” – Patricia Fripp
Features of Personal selling
(i) Personal form In personal selling a direct face to face dialogue takes place that involves an interactive relationship between the seller and the buyer.
(ii) Development of Relationship Personal selling allows a sales person to develop personal relationship with the prospective customers, which may become important in making sale.
![]()
Difference between Advertising and Personal selling
The major differences between advertising and personal selling are as follows
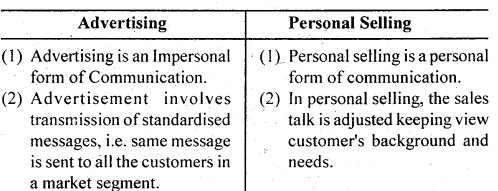

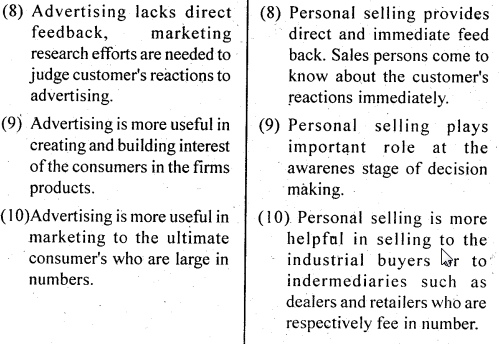
![]()