Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Questions and Answers Provided helps you to answer complex Questions too easily. You can use them while preparing for board exams and all of them are given by subject experts. Reading NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries familiarizes you with the kind of questions appearing in the board exams. Students are advised to read these solutions on a regular basis to score well.
Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Questions and Answers Geography Chapter 6
Make your learning experience enjoyable by preparing from the quick links available on this page. Use the Class 10 SST Geography Chapter 6 NCERT Solutions and get to know different concepts involved. All the Solutions are covered as per the latest syllabus guidelines. Knowing the NCERT Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Questions and Answers helps students to attempt the exam with confidence.
Manufacturing Industries NCERT Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why did Mahatma Gandhi lay emphasis on spinning yarn and weaving khadi
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi in order to promote swadeshi goods encouraged the people to spin yarn and weave khadi. During the colonial period, the British had uprooted the Indian textile industries by replacing them with the British mill-made goods especially the textiles. This adversely affected the weavers. They lost their livelihood due to the closure of several Indian handloom industries. So, Gandhiji encouraged Indians to spin yam and weave khadi. This served twin purposes – it spread nationalism and provided work to poor artisans and weavers.
![]()
Question 2.
Why is it important for our country to keep the mill sector loomage lower than powerloom and handloom?
Answer:
It is because powerlooms and handlooms are the tools of the poor artisans and weavers in India with which they earn their livelihood. If the mill sector loomage is encouraged, it will affect them adversely. They will lose their livelihood. So keeping the welfare of these poor artisans and weavers in mind, it is important to keep mill sector loomage lower than powerloom and handloom.
Question 3.
Why is it important for us to improve our weaving sector instead of exporting yarn in large quantities?
Answer:
Weaving is highly decentralised to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery,etc. India has world class production in spinning, but weaving supplies low quality of fabric as it cannot use much of the high quality yarn produced in the country. Weaving is done by handloom, powerloom and in mills. The handspun khadi provides large scale employment to weavers in their homes as a cottage industry.
Question 4.
Why is the per capita consumption of steel so low in India?
Answer:
- A major portion of population lives in villages. They lead a poor life and therefore, they have less requirement for steel due to its high cost.
- Lack of adequate means of transport makes it difficult to deliver steel in India’s remote areas.
- Lack of infrastructure as a result of which modern and cost effective technologies for steel production are not utilised.
- Most of the steel produced in India is exported. In 2004, the country was the largest exporter of steel which accounted for 2.25 percent of the global steel trade.
![]()
Geography Class 10 Chapter 6 NCERT Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Multiple Choice Questions
(i) Which one of the following industries uses limestone as a raw material?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Cement
(c) Sugar
(d) Jute
Answer:
(b) Cement
(ii) Which one of the following agencies markets steel for the public sector plants?
(a) HAIL
(b) SAIL
(c) TATA Steel
(d) MNCC
Answer:
(b) SAIL
(iii) Which one of the following industries uses bauxite as a raw material?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Cement
(c) Jute
(d) Steel
Answer:
(a) Aluminium
![]()
(iv) Which one of the following industries manufactures telephones, computer, etc.
(a) Steel
(b) Aluminium
(c) Electronic
(d) Information technology
Answer:
(c) Electronic
Question 2.
Answer the following briefly in not more than 30 words.
(i) What is manufacturing?
Answer:
Manufacturing is production of goods in large quantities after processing from raw materials to more valuable products.
For example, sugar is manufactured from sugarcane, iron and steel from iron ore, etc.
(ii) Name any three physical factors for the location of the industry.
Answer:
(a) Availability of raw material
(b) Availability of water and power supply
(c) Availability of transport facilities
(iii) Name any three human factors for the location of an industry.
Answer:
(a) Availability of labour/specialised labour
(b) Market
(c) Government policies.
(iv) What are basic industries? Give an example.
Answer:
Industries that supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other goods are called basic or key industries. For example, iron and steel, copper smelting and aluminum smelting etc.
![]()
(v) Name the important raw materials used in the manufacturing of cement.
Answer:
(a) Limestone
(b) Silica
(c) Alumina, and
(d) Gypsum
Question 3.
Write the answers of the following questions in 120 words.
(i) How are integrated steel plants different from mini steel plants? What problems does the industry face? What recent developments have led to a rise in the production capacity?
Answer:
Integrated steel plants are large which handle everything in one complex from putting together raw material to steel making, rolling and shaping. So far mini steel plants are concerned, they are smaller, have electric furnaces, use steel scrap and sponge iron. They have re-rollers that use steel ingots as well. They produce mild and alloy steel of given specifications. The industry faces several problems. Some of them are:
- High costs and limited availability of coking coal.
- Lower productivity of labour
- Irregular supply of power
- Poor infrastructure
Liberalisation and foreign direct investment (FDI) have given a boost to the industry with the efforts of private entrepreneurs. There is a need to allocate resources for research and development to produce steel more efficiently.
![]()
(ii) How do industries pollute the environment?
Answer:
Although industries contribute significantly to India’s economic growth and development, they also cause environmental degradation to a great extent. The increase in pollution of land, water, air and noise due to industries cannot be ignored. Industries are responsible for four types of pollution-air, water, land and noise. The polluting industries also include thermal power plants.
(a) Air pollution is caused by the presence of high proportion of undesirable gases, such as sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide. Air borne particulate materials contain both solid and liquid particles like dust, sprays mist and smoke. Smoke is emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries and smelting plants and burning of fossil fuels in factories.
(b) Water pollution is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and effluents discharged into rivers.
(c) Thermal pollution of water occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
(d) Soil and water pollution are closely related. Dumping of wastes specially glass, harmful chemicals, industrial effluents, packaging, salts and garbage renders the soil useless.
(e) Rainwater percolates to the soil carrying the pollutants to the ground and the ground water also gets contaminated.
(f) Noise pollution is caused due to industrial and construction activities, factory equipment, machinery, generators, and electric saws and drills.
![]()
(iii) Discuss the steps to be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry.
Answer:
The following steps can be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry:
(a) Minimising use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it in two or more successive stages.
(b) Harvesting of rainwater to meet water requirements.
(c) Treating hot water and effluents before releasing them in rivers and ponds.
Treatment of industrial effluents can be done in three phases:
- Primary treatment by mechanical means. This involves screening, grinding, flocculation and sedimentation.
- Secondary treatment by biological process.
- Tertiary treatment by biological, chemical and physical processes. This involves recycling of wastewater.
(d) Particulate matter in the air can be reduced by fitting smoke stacks to factories with electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators.
(e) Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Machinery can be redesigned to increase energy efficiency and reduce noise.
![]()
Activity
Give one word for each of the following with regard to industry. The number of letters in each word are hinted in brackets.

Answer:
(i) POWER
(ii) WORKER
(iii) MARKET
(iv) RETAILER
(v) PRODUCT
(vi) MANUFACTURE
(vii) POLLUTION
Project Work
Select one agro-based and one mineral based industry in your area.
(i) What are the raw materials they use?
(ii) What are the other inputs in the process of manufacturing that involve transportation cost?
(iii) Are these factories following environmental norms?
Answer:
Do it yourself.
![]()
Activity
Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
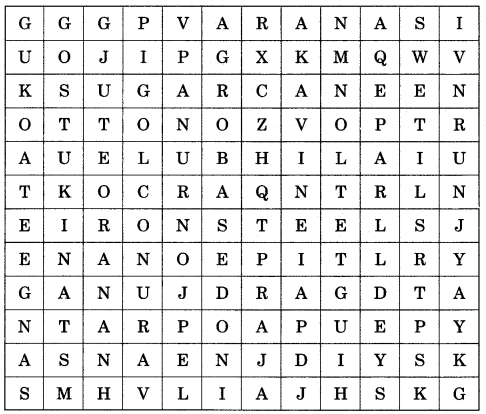
1. Textiles, sugar, vegetable oil and plantation industries deriving raw materials from agriculture are called…
2. The basic raw material for sugar industry.
3. This fibre is also known as the ‘ Golden Fibre’.
4. Iron-ore, coking coal, and limestone are the chief raw materials of this industry.
5. A public sector steel plant located in Chhattisgarh.
6. Railway diesel engines are manufactured in Uttar Pradesh at this place.
Answer:
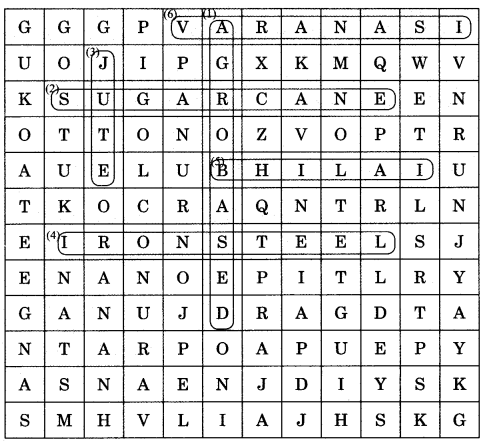
1. Agro-based
2. Sugarcane
3. Jute
4. Iron and steel
5. Bhilai
6. Varanasi
Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 NCERT Intext Activity Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Classify the following into two groups on the basis of bulk and weight of raw material and finished goods.
(i) Oil
(ii) Knitting needles
(iii) Brassware
(iv) Fuse wires
(v) Watches
(vi) Sewing machines
(vii) Ship building
(viii) Electric bulbs
(ix) Paint brushes
(x) Automobiles
| Light Industries | Heavy Industries |
| (i) Knitting needles (ii) Brassware (iii) Fuse wires (iv) Watches (v) Sewing machines (vi) Electric bulbs (vii) Paint brushes |
(i) Oil (ii) Ship building (iii) Automobiles |
Question 2.
Make a list of all such goods made of steel that you can think of.
Answer:
- Utensils (glass, bowls, dishes, etc.)
- Tools (screw driver, stapler, etc.)
- Gates
- Paper clips, staples, rulers, and file cabinets
- Automobiles, trains and ships
- Surgical equipments
- Major appliances (washing machines, refrigerators, etc.)
- Cutlery sets.
Question 3.
Where would it be economically viable to set up the cement manufacturing units?
Answer:
The cement industry requires bulky and heavy raw materials like limestone, silica, alumina and gypsum. Therefore, this industry should be set up close to the areas where such minerals are found. This would reduce the cost of transportation of these materials. Apart from rail transportation regular availability of electric power is also taken into consideration while setting up the cement manufacturing units.
Question 4.
Find out where the cement manufacturing plants are located in other states of India. Find their names.
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Delhi, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal.
Hope the data shared above regarding the NCERT Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries PDF has aided in your exam preparation. If you ever need any assistance you can always reach us and our team will guide you at the soonest possibility.