Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Questions and Answers Provided helps you to answer complex Questions too easily. You can use them while preparing for board exams and all of them are given by subject experts. Reading NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources familiarizes you with the kind of questions appearing in the board exams. Students are advised to read these solutions on a regular basis to score well.
Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Questions and Answers Geography Chapter 5
Make your learning experience enjoyable by preparing from the quick links available on this page. Use the Class 10 SST Geography Chapter 5 NCERT Solutions and get to know different concepts involved. All the Solutions are covered as per the latest syllabus guidelines. Knowing the NCERT Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Questions and Answers helps students to attempt the exam with confidence.
Minerals and Energy Resources NCERT Intext Questions and Answers
(Dig a Little Deeper)
Question 1.
Find out how many minerals are used to make a light bulb?
Answer:
Minerals used to make different parts of a light bulb are-
Parts of a light bulb – Minerals used
- Filament – tungsten
- Bulb – glass
- Connecting wires – copper
- Metallic part of body – aluminium
![]()
Question 2.
Collect ‘nutritional facts’ printed on food labels.
Answer:
A sample of nutritional facts printed on a packet of salty biscuits (Patanjali Jeera Bites) is given below:
| Calories | 99 Kcal |
| Total fat | 4.25 gm |
| Cholesterol | Nil |
| Protein | 1.75 gm |
| Total carbohydrate | 13 gm |
| Dietary fibre | 1 gm |
| Sugar | 2 gm |
Question 3.
What is the difference between an open-pit mine, a quarry and an underground mine with shafts?
Answer:
| Open Pit Mine | Quarry | Underground Mine with shafts |
| 1. Minerals are removed from a pit dug in the ground. | 1. Minerals are removed from a shallow pit dug in the ground. | 1. Minerals are removed through deep shafts dug in the ground. |
| 2. Open pit mine is used where commercially useful minerals are found near the surface. | 2. Quarry is generally used for extracting building materials. | 2. It is used where the mineral occurs as veins in hard rock deep below the surface of the Earth. |
Question 4.
Superimpose the maps showing distribution of iron ore, manganese, coal and iron and steel industry. Do you see any correlation? Why?
Answer:
The iron and steel industries are located in the same regions of India where the iron ore, coal and manganese mines are located. As coal and manganese are required as inputs to the iron and steel industry, their availability in the same region saves on transportation costs as well as on ease of availability. Thus, it is profitable to locate these industries in the regions where these minerals are found.
![]()
Question 5.
Locate the mines of bauxite on the physical map of India.
Answer:
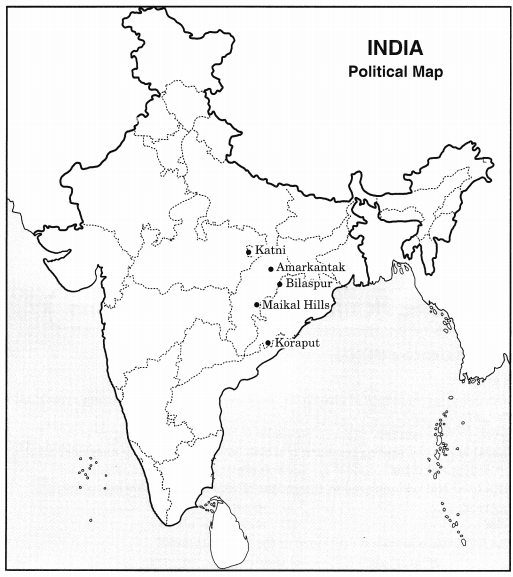
Question 6.
Study the maps to explain why Chota Nagpur is a storehouse of minerals.
Answer:
Chota Nagpur is a storehouse of minerals because of the following reasons
- About 40% of iron ore in India is found in this region.
- About 50% of manganese in India is found in this region.
- Almost 60% of copper and the same percentage of bauxite in India are found here.
- Coal is also available in this area in abundance.
- Other minerals found in this region are limestone, zinc, lead, etc.
![]()
Question 7.
Make a list of items where substitutes are being used instead of minerals. Where are these substitutes obtained from?
Answer:
Natural gas and oil may be the substitute of coal. Wood or plastic may be substitute of steel, iron and copper.
Geography Class 10 Chapter 5 NCERT Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Choose the correct answer:
(i) Which one of the following minerals is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass of weathered material?
(a) coal
(b) bauxite
(c) gold
(d) zinc
Answer:
(a) coal
(ii) Koderma, in Jharkhand is the leading producer of which one of the following minerals?
(a) bauxite
(b) mica
(c) iron ore
(d) copper
Answer:
(b) mica
![]()
(iii) Minerals are deposited and accumulated in the stratas of which of the following rocks?
(a) sedimentary rocks
(b ) metamorphic rocks
(c) igneous rocks
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) sedimentary rocks
(iv) Which one of the following minerals is contained in the Monazite sand?
(a) oil
(b) uranium
(c) thorium
(d) coal
Answer:
(c) thorium
Question 2.
Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Distinguish between the following in not more than 30 words.
(a) ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
(b) conventional and non-conventional sources of energy
Answer:
(a) Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
| Ferrous minerals | Non-ferrous minerals |
| (i) The minerals having iron contents are called ferrous minerals. | (i) The minerals having no iron contents are called non-ferrous minerals. |
| (ii) India is rich in ferrous minerals. | (ii) India’s reserves and production of non-ferrous minerals is not satisfactory. |
| (iii) Example- iron ore, nickel, cobalt, manganese, etc. | (iii) Example- copper, lead, tin, bauxite, etc. |
![]()
(b) conventional and non-conventional sources of energy
| Conventional sources of energy | Non-conventional sources of energy |
| (i) Conventional sources of energy have been in use from ages. | (i) Non-conventional sources of energy have been identified in the recent past. |
| (ii) These are non-renewable sources of energy. | (ii) These are renewable sources of energy. |
| (iii) They cause air and water pollution. | (iii) They are environment-friendly i.e. they do not cause pollution. |
| (iv) Example- coal, petroleum, firewood, cattle dung cake, natural gas, etc. | (iv) Example- solar wind, tidal, geothermal, biogas and atomic energy. |
(ii) What is a mineral?
Answer:
Mineral is a homogenous, naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure. Minerals are found in varied forms in nature, ranging from the hardest diamond to the softest talc.
(iii) How are minerals formed in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
Answer:
In igneous and metamorphic rocks, minerals occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints. The smaller occurrences are called veins and the larger are called lodes. In most cases, they are formed when minerals in liquid / molten and gaseous forms are forced upwards through cavities towards the earth’s surface. Metallic minerals like tin, copper, zinc and lead etc. are obtained from veins and lodes.
![]()
(iv) Why do we need to conserve mineral resources?
Answer:
- It takes millions of years for the formation of minerals.
- The geological processes of mineral formation are so slow that the rates of replenishment are infinitely small in comparison to the present rates of consumption.
- Mineral resources are finite and non-renewable. We can easily infer from the above points that conservation of mineral resources is essential.
Question 3.
Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Describe the distribution of coal in India.
Answer:
In India, coal occurs in rock series of two main geological areas, namely Gondwana, a little over 200 million years in age and in tertiary deposits which are only about 55 million years old.
- Gondwana coal is located in Damodar valley (West Bengal-Jharkhand). Jharia, Raniganj, Bokaro, etc., are important coalfields. The Godavari, Mahanadi, Son and Wardha valleys also contain coal deposits.
- Tertiary coal occurs in the north-eastern states of Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
(ii) Why do you think that solar energy has a bright future in India?
Answer:
India being a tropical country has great possibilities of tapping solar energy. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. Solar energy is becoming popular in rural and remote areas of India fastly. It can help in minimising the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes. It can also help in conservation of fossil fuels. Adequate supply of manure in agriculture can also be possible, when dependence on dung cakes is minimised.
Activity
Fill the name of the correct mineral in the crossword below:
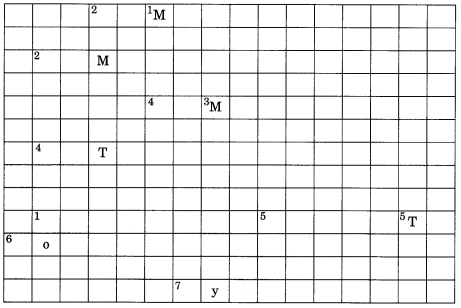
ACROSS
1. A ferrous mineral (9)
2. Raw material for cement industry (9)
3. Finest iron ore with magnetic properties (9)
4. Highest quality hard coal (10)
5. Aluminium is obtained from this ore (7)
6. Khetri mines are famous for this mineral (6)
7. Formed due to evaporation (6)
DOWN
1. Found in placer deposit (4)
2. Iron ore mined in Bailadila (8)
3. Indispensable for electrical industry (4)
4. Geological Age of coal found in north east India (8)
5. Formed in veins and lodes (3)
ACROSS – DOWN
1. Manganese – 1. Gold
2. Limestone – 2. Hematite
3. Magnetite – 3. Mica
4. Anthracite – 4. Tertiary
5. Bauxite – 5. Tin
6. Copper
7. Gypsum
![]()
Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 NCERT Intext Activity Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name some river valley projects and write the names of the dams built on these rivers.
Answer:
| Name of River Valley Projects | Name of Dams |
| (i) Bhakra Nangal Project on river Sutlej | Bhakra and Nangal dams |
| (ii) Mahanadi River Project | Hirakud dam |
| (iii) Chambal Valley Project | Gandhi Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, and Jawahar Sagar dam |
| (iv) Tungabhadra River Project | Tungabhadra dam |
| (v) Rihand project on River Son | Rihand dam |
![]()
Question 2.
Collect information about newly established solar power plants in India.
Answer:
The newly established solar power plants in India are-
- Phalodhi (Rajasthan)
- Patapur (Odisha)
- Neemuch (Madhya Pradesh)
- Pokharan, Badma (Rajasthan)
Hope the data shared above regarding the NCERT Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources PDF has aided in your exam preparation. If you ever need any assistance you can always reach us and our team will guide you at the soonest possibility.