If you’re looking for a way to enhance your Class 9 Maths, then look no further than the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles with Answers. MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths with Answers is perfect for those who are in Class 9 Maths and want to get ahead of everyone else by mastering the subject skills as soon as possible! Go ahead and find Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles Objective Questions.
Triangles Class 9 MCQs Questions with Answers
Solving MCQ on Triangles Multiple Choice Questions of Class 9 Maths with Answers can be of great help to students as they will be aware of all the concepts. These Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 MCQ with Answers pave for a quick revision, thereby helping you learn more about this subject.
Question 1.
△ABC = △PQR, then which of the following is true?
(a) CB = QP
(b) CA = RP
(c) AC = RQ
(d) AB = RP
Answer
Answer: (b) CA = RP
Question 2.
In △ABC and △DEF, AB = DE and ∠A = ∠D.Then two triangles will be congruent by SA axiom if:
(a) BC = EF
(b) AC = EF
(c) AC = DE
(d) BC = DE
Answer
Answer: (c) AC = DE
Question 3.
In a right triangle, the longest side is:
(a) Perpendicular
(b) Hypotenuse
(c) Base
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Hypotenuse
Question 4.
In △ABC, if ∠A = 45° and ∠B = 70°, then the shortest and the longest sides of the triangle are respectively,
(a) BC,AB
(a) AB,AC
(c) AB,BC
(d) BC,AC
Answer
Answer: (d) BC,AC
Question 5.
If the altitudes from vertices of a triangle to the opposite sides are equal, then the triangles is
(a) Scalene
(b) Isosceles
(c) Equilateral
(d) Right-angled
Answer
Answer: (b) Isosceles
Question 6.
D is a Point on the Side BC of a △ABC such that AD bisects ∠BAC then:
(a) BD = CD
(b) CD > CA
(c) BD > BA
(d) BA > BD
Answer
Answer: (d) BA > BD
Question 7.
If ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR then which of the following is true:
(a) CA = RP
(b) AB = RP
(c) AC = RQ
(d) CB = QP
Answer
Answer: (a) CA = RP
Question 8.
If two triangles ABC and PQR are congruent under the correspondence A ↔ P, B ↔ Q, and C ↔ R, then symbolically, it is expressed as
(a) ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
(b) ΔABC = ΔPQR
(c) ΔABC and ΔPQR are scalene triangles
(d) ΔABC and ΔPQR are isosceles triangles
Answer
Answer: (a) ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR
Question 9.
If the bisector of the angle A of an △ABC is perpendicular to the base BC of the triangle then the triangle ABC is :
(a) Obtuse Angled
(b) Isosceles
(c) Scalene
(d) Equilateral
Answer
Answer: (b) Isosceles
Question 10.
If AB = QR, BC=RP and CA = QP, then which of the following holds?
(a) △BCA ≅ △PQR
(b) △ABC ≅ △PQR
(c) △CBA ≅ △PQR
(d) △CAB ≅ △PQR
Answer
Answer: (d) △CAB ≅ △PQR
Question 11.
ABC is an isosceles triangle in which altitudes BE and CF are drawn to equal sides AC and AB respectively. Then:
(a) BE > CF
(b) BE < CF
(c) BE = CF
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) BE = CF
Question 12.
Which of the following is not a criterion for congruence of triangles?
(a) SSS
(b) SSA
(c) ASA
(d) SAS
Answer
Answer: (b) SSA
Question 13.
In △ABC, if ∠B = 30° and ∠C = 70°, then which of the following is the longest side?
(a) AB
(b) BC
(c) AC
(d) AB or AC
Answer
Answer: (b) BC
Question 14.
The angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are:
(a) Equal
(b) Unequal
(c) supplementary angles
(d) Complementary angles
Answer
Answer: (a) Equal
Question 15.
If ABC is an equilateral triangle, then each angle equals to:
(a) 90°
(b)180°
(c) 120°
(d) 60°
Answer
Answer: (d) 60°
Question 16.
ABC ≅ △PQR. If AB=5 cm, and then which of the following is true?
(a) QR = 5 CM, ∠R= 60°
(b) QP = 5 cm, ∠P= 60°
(c) QP = 5cm, ∠R = 60°
(d) QR = 5 CM, ∠Q = 60°
Answer
Answer: (b) QP = 5 cm, ∠P= 60°
Question 17.
O is any point in the interior of △ABC.Then which of the following is true?
(a) (OA+OB+OC) < \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (AB+BC+CA)
(b) (OA+OB+OC) > (AB+BC+CA)
(c) (OA+OB+OC) > \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (AB+BC+CA)
(d) None of the Above
Answer
Answer: (c) (OA+OB+OC) > \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (AB+BC+CA)
Question 18.
It is not possible to construct a triangle when its sides are:
(a) 6 cm, 7 cm, 7 cm
(b) 5.4 cm, 2.3 cm, 3 cm
(c) 8.3 cm, 3.4 cm, 6.1 cm
(d) 3 cm, 5 cm, 5 cm
Answer
Answer: (b) 5.4 cm, 2.3 cm, 3 cm
Question 19.
Two equilateral triangles are congruent when:
(a) Their areas are proportional
(b) Their sides are equal
(c) Their sides are proportional
(d) Their angles are equal
Answer
Answer: (b) Their sides are equal
Question 20.
It is not possible to construct a triangle when the lengths of its sides are
(a) 4 cm, 6 cm, 6 cm
(b) 9.3 cm, 5.2 cm, 7.4 cm
(c) 6 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm
(d) 5.3 cm, 2.2 cm, 3.1 cm
Answer
Answer: (d) 5.3 cm, 2.2 cm, 3.1 cm
Question 21.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) Two squares having the same side length are congruent
(b) Two rectangles having the same area are congruent
(c) Two circles having the same radius are congruent
(d) Two lines having same length are congruent
Answer
Answer: (b) Two rectangles having the same area are congruent
Question 22.
ABCD is a parallelogram, if the two diagonals are equal, then by what criterion are the triangles ABD and ABC congruent
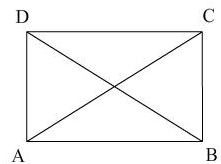
(a) AAS
(b) SSS
(c) SAS
(d) RHS
Answer
Answer: (b) SSS
Hope you found this information on NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles with Answers useful. We are always here to help, so if there is any specific query or question with CBSE Class 9 Maths Triangles MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers or any other topic please let us know in the comments below.