If you’re looking for a way to enhance your Social Science, then look no further than the NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 History Chapter 7 Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Social Science with Answers is perfect for those who are in class 8 and want to get ahead of everyone else by mastering their subject skills as soon as possible! So, ace up your preparation with MCQ of Chapter 7 History Objective Questions.
Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners Class 8 MCQs Questions with Answers
Solving MCQ on Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners Class 8 with Answers can be of great help to students as they will be aware of all the concepts. These Class 8 SST History Chapter 7 MCQ with Answers pave for a quick revision, thereby helping you learn more about this subject.
Question 1.
European encountered just fine cloth from India carried by the Arab merchants and they named the cloth as:
(a) Bandanna
(b) Calica
(c) Muslin
(d) Patola
Answer
Answer: (c) Muslin
Question 2.
Which of the following was woven in Surat, Ahmedabad and Patan and valued in Indonesia?
(a) Patola
(b) Muslin
(c) Calico
(d) Jamdani
Answer
Answer: (a) Patola
Question 3.
In 1764, name the person who invented the spinning jenny.
(a) Wellesley
(b) Dorabji
(c) Charles Weld
(d) John Kaye
Answer
Answer: (d) John Kaye
Question 4
Which among the following is a household spinning instrument?
(a) Armour
(b) Takli
(c) Khadi
(d) Tanti
Answer
Answer: (b) Takli
Question 5.
Which country from 1850’s came to be known as ‘workshop of the world’?
(a) England
(b) India
(c) Japan
(d) Africa
Answer
Answer: (a) England
Question 6.
What are the important centers of Jamdani weaving in India?
(a) Dhaka (Dacca)
(b) Murshidabad
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Both a and b
Jamdani weave, early twentieth century Jamdani is fine muslin on which decorative motifs are woven on the loom, typically in grey and white.
Question 7.
In which area Agarias were specialized in?
(a) wearing
(b) iron smelting
(c) mine working
(d) dyeing cloth
Answer
Answer: (b) iron smelting
Agarias a community living in central India was specialized in iron smelting.
Question 8.
Who was Chhipigars?
(a) Weavers
(b) Cotton growers
(c) Dyers
(d) Block printers
Answer
Answer: (d) Block printers
For printed cloth the weavers needed the help of specialist block printers known as chhipigars. Handloom weaving and the occupations associated with it provided livelihood for millions of Indians.
Question 9.
Which type of cloth considers Chintz, cossaes, khassa, bandanna?
(a) Silk cloth
(b) Jute cloth
(c) Cotton coloured cloth
(d) Printed cotton cloth
Answer
Answer: (d) Printed cotton cloth
The pieces ordered in bulk were printed cotton cloths called chintz, cossaes (or khassa) and bandanna.
Question 10.
In which state did Patola was not woven?
(a) Surat
(b) Ahmedabad
(c) Patna
(d) Sabarmati
Answer
Answer: (d) Sabarmati
Patola was woven in Surat, Ahmedabad and Patan. Highly valued in Indonesia, it became part of the local weaving tradition there.
Question 11.
From where did Britain import raw materials for its cotton industries?
(a) India
(b) Japan
(c) America
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (a) India
Most of the raw material for the cotton industries was imported from India.
Question 12.
Who are Agaria?
(a) Person carrying Cotton
(b) Person carrying wood
(c) Person carrying iron ore
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Person carrying iron ore
The group of men and women carrying basket loads of iron ores in regions of control India were called as Agarias.
Question 13.
What is Jamdani?
(a) Fine muslin
(b) Fine cotton
(c) Fine silk
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Fine muslin
Jamdani is fine muslin on which decorative motifs are woven on the loom, typically in grey and white. Often a mixture of cotton and gold thread was used.
Question 14.
Why Britain was referred to as the workshop of the world?
(a) Selling of indigo
(b) Trading of Iron
(c) Buying of cotton
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Trading of Iron
Britain was referred to as the workshop of the world as its iron and steel industries started growing from 1850s and gained success. So many started buying and selling Iron from Britain in greater quantities and thus it was given the title ‘workshop of world’.
Question 15.
Mention the industries which were crucial for the industrial revolution in England.
(a) Textiles
(b) Steel
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Both a and b
The two industries which were crucial for the industrial revolution in England were Textiles and Iron and Steel.
Question 16.
When did the craft of Iron smelting in India decline?
(a) 18th century
(b) 19th century
(c) 20th century
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) 19th century
By the late nineteenth century, the craft of iron smelting was in decline. When the colonial government prevented people from entering the reserved forests it also affect the iron textile.
Question 17.
Tipu sultan’s sword is made up of which metal?
(a) Wood
(b) Wootz
(c) Glass
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Wootz
Tipu sultan sword came from a special type of high carbon steel called Wootz which was produced all over South India. Wootz steel when made into swords produces a very sharp edge with a flowing water pattern.
Question 18.
Why was the sword of Tipu Sultan very popular?
(a) He died with his sword in his hand
(b) He never lose any war
(c) He sold his sword to British
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) He died with his sword in his hand
Tipu Sultan ruled Mysore till 1799, fought four wars with the British and died fighting with his sword in his hand. Tipu’s legendary swords are now part of valuable collections in museums in England.
Question 19.
When was the spinning jenny invented?
(a) 1768
(b) 1793
(c) 1742
(d) 1764
Answer
Answer: (d) 1764
In 1764, the spinning jenny was invented by James Hargreaves which increased the productivity of the traditional spindles.
Question 20.
Who invented the spinning jenny?
(a) Richard Ark Wright
(b) James Hargreaves
(c) James Thomas
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) James Hargreaves
In 1764, the spinning jenny was invented by James Hargreaves which increased the productivity of the traditional spindles.
Write true (T) or false (F)
1. Indian wootz steel fascinated the European scientists.
Answer
Answer: True
2. Francis Buchanan who toured Bombay in 1800 after Tipu Sultan left an technique by which Wootz steel was produced.
Answer
Answer: True
3. The development of cotton textiles in Britain affected textiles producers in India.
Answer
Answer: True
4. First cotton mill in India was set up as a spinning mill in Bombay in 1854.
Answer
Answer: True
5. Production of Wootz steel required a highly specialised technique of refining cloths.
Answer
Answer: False
Match the following
1.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| 1. Device to pump air | (a) Kannada- Ukku |
| 2. Wootz | (b) Slag heaps |
| 3. TISCO | (c) Bellows |
| 4. Waste left when smelting metal | (d) 1912 |
| 5. Ist World War | (e) 1914 |
Answer
Answer:
| Column-I | Column-II |
| 1. Device to pump air | (c) Bellows |
| 2. Wootz | (a) Kannada- Ukku |
| 3. TISCO | (d) 1912 |
| 4. Waste left when smelting metal | (b) Slag heaps |
| 5. Ist World War | (e) 1914 |
Fill in the blanks
1. Khadi gradually became a symbol of ……………………… .
Answer
Answer: Nationalism
2. For coloured textiles, the thread was dyed by the dyer known as ……………………… .
Answer
Answer: Rangrez
3. In ……………………… the spinning jenny was invented by John Kaye.
Answer
Answer: 1764
4. The ……………………… developed and the industrial class became stronger.
Answer
Answer: Nationalist Movement
5. ……………………… hills had one of the finest ores in the world.
Answer
Answer: Rajhara
6. The smelting was done by men while women worked the ………………………, pumping air that kept the charcoal
burning.
Answer
Answer: Bellows
Picture Based Questions
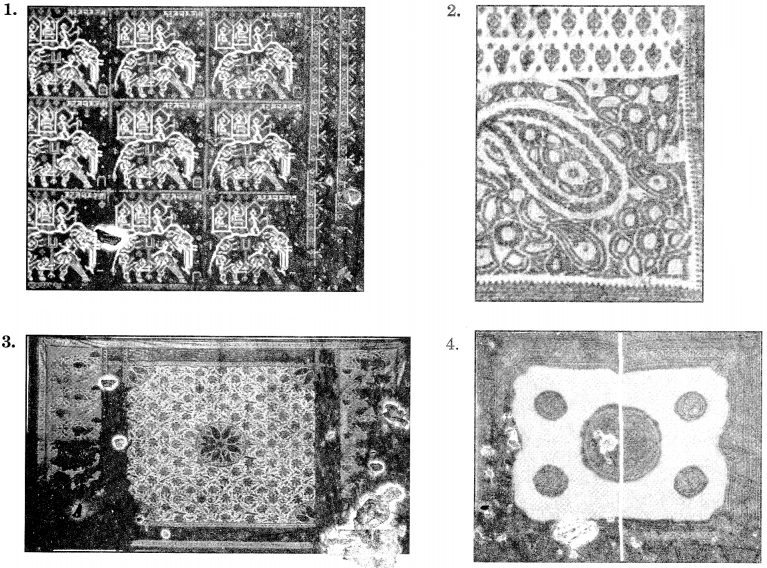
Answer
Answer:
1. Patola weaves 2. Jamdani weaves
3. Chintz weaves 4. Vandana weaves
Map Skills
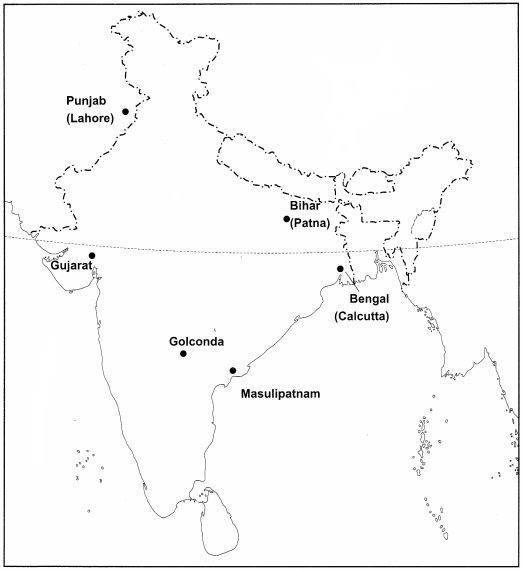
On an outline map of India represent the following which shows the major centres of weaving in the late 18th century.
(i) Punjab (Lahore) (ii) Gujarat (iii) Bengal (Culcutta)
(iv) Bihar (Patna) (v) Golconda (vi) Masulipatnam
Answer
Answer:
Hope you found this information on NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 History Chapter 7 Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners with Answers Pdf free download useful. We are always here to help, so if there is any specific query or question with CBSE Social Science Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners Class 8 MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers or any other topic please let us know in the comments below.