Do you need help learning for your Class 12 Physics exam? Students may want to download NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments with Answers Pdf free download. This Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 MCQs Questions with Answers can help understand the concepts score better in your Class 12 Physics Exam, so make sure you practice these! Check out chapter-wise MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics with Answers.
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 MCQs Questions with Answers
Solve this Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Multiple Choice Questions of Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 MCQ, so as not to miss out on any concept from being clear about what they mean!
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Ashort pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab atnormal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is
(a) blue.
(b) green.
(c) violet.
(d) red.
Answer
Answer: (d) red.
Question 2.
You are given four sources of light each one providing a light of a single colour – red, blue, green and yellow. Suppose the angle of refraction for a beam of yellow light corresponding to a particular angle of incidence at the interface of two media is 90°. Which of the following statements is correct if the source of yellow light is replaced with that of other lights without changing the angle of incidence?
(a) The beam of red light would undergo total internal reflection.
(b) The beam of red light would bend towards normal while it gets refracted through the second medium.
(c) The beam of blue light would undergo total internal reflection.
(d) The beam of green light would bend away from the normal as it gets refracted through the second medium.
Answer
Answer: (c) The beam of blue light would undergo total internal reflection.
Question 3.
The optical density of turpentine is higher than that of water while its mass density is lower. Figure shows a layer of turpentine floating over water in a container. For which one of the four rays incident on turpentine in figure, the path shown is correct?
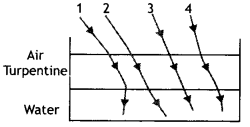
(a) 1.
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (b) 2
Question 4.
There are certain material developed in laboratories which have a negative refractive index (figure). A ray incident from air (medium 1) into such a medium (medium 2) shall follow a path given by
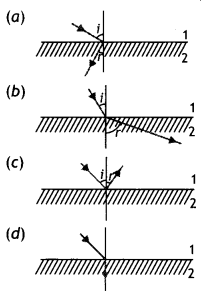
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 5.
Consider an extended object immersed in water contained in a plane trough. When seen from close to the edge of the trough the object will not look distorted because
(a) the apparent depth of the points close to the edge are nearer the surface of the water compared to the points away from the edge.
(b) the angle subtended by the image of the object at the eye is smaller than the actual angle subtended by the object in air.
(c) some of the points of the object far away from the edge may not be visible because of total internal reflection.
(d) water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
Answer
Answer: (d) water in a trough acts as a lens and magnifies the object.
Question 6.
A rectangular block of glass ABCD has a refractive index 1.6. A pin is placed midway on the face AB (figure). When observed from the face AD, the pin shall
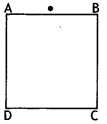
(a) appear to be near A.
(b) appear to be near D.
(c) appear to be at the centre of AD.
(d) not be seen at all.
Answer
Answer: (d) not be seen at all.
Question 7.
An astronomical refractive telescope has an objective of focal length 20 m and an eyepiece of focal length 2 cm. Which one of the following is not possible?
(a) The length of the telescope tube is 20.02 m.
(b) The magnification is 1000.
(c) The image formed is inverted.
(d) An objective of a larger aperture will increase the brightness and reduce chromatic aberration of the image.
Answer
Answer: (d) An objective of a larger aperture will increase the brightness and reduce chromatic aberration of the image.
Question 8.
An object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. If the object is displaced through a distance of 20 cm towards the mirror, the displacement of the image will be:
(a) 30 cm away from the mirror
(b) 36 cm away from the mirror
(c) 30 cm towards the mirror
(d) 36 cm towards the mirror
Answer
Answer: (b) 36 cm away from the mirror
Question 9.
The refractive index of the material of a prism is √2 and the angle of the prism is 30°. One of the two refracting surfaces of the prism is made a mirror inwards, by silver coating. A beam of monochromatic light entering the prism from the other face will retrace its path (after reflection from the silvered surface) if its angle of incidence on the prism is:
(a) 60°
(b) 45°
(c) 30°
(d) zero
Answer
Answer: (b) 45°
Question 10.
A diverging lens with magnitude of focal length 25 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a converging lens of magnitude of focal length 20 cm. A beam of parallel light falls on the diverging lens. The final image formed is:
(a) real and at a distance of 40 cm from the divergent lens
(b) real and at a distance of 6 cm from the convergent lens
(c) real and at a distance of 40 cm from convergent lens
(d) virtual and at a distance of 40 cm from convergent lens.
Answer
Answer: (c) real and at a distance of 40 cm from convergent lens
II. Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
The bouncing back of light when it strikes a smooth or polished surface is called …………….. of light.
Answer
Answer: Reflection
Question 2.
When light is reflected from a polit, surface the angle of incidence is …………… to the angle of reflection.
Answer
Answer: Equal
Question 3.
The image formed by a plane mirror shows …………….. inversion.
Answer
Answer: Lateral
Question 4.
A plane drawn perpendicular to the principal axis and passing through the principal focus is called ………………. plane.
Answer
Answer: Focal
Question 5.
The size of the mirror is called its …………………..
Answer
Answer: Aperture
Question 6.
The focal length of a spherical mirror is ……………….. its radius of curvature.
Answer
Answer: Half
Question 7.
…………….. mirror is used as a rear-view mirror in automobiles.
Answer
Answer: Convex
Question 8.
A real image ………………… be focused on a screen.
Answer
Answer: Can
Question 9.
A virtual image ……………… be focused or e screen.
Answer
Answer: Cannot
Question 10.
The mirror formula is ……………….
Answer
Answer: \(\frac { 1 }{f}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{u}\) + \(\frac { 1 }{v}\)
Question 11.
The magnification produced by a spherical mirror is given by …………….
Answer
Answer: m = –\(\frac { v }{u}\)
Question 12.
If m is ………………. the image is erect w.r,t the object.
Answer
Answer: Positive
Question 13.
If m is ……………….. the image is inverted w.r.t. the object.
Answer
Answer: Negative
Question 14.
The basic cause of refraction is change in ………………… of light in going from one medium to another.
Answer
Answer: Velocity
Question 15.
……………… of light does not change when a ray of light moves from an optically rarer to an optically denser medium.
Answer
Answer: Frequency
Question 16.
An air bubble in a jar of water shines brightly is an example of …………………
Answer
Answer: Total Internal Reflection
Question 17.
For the same angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three different mediums A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively, ……………. medium will the velocity of light be minimum.
Answer
Answer: A
Question 18.
Total internal reflection must occur when angle of incidence is more than the …………………
Answer
Answer: Critical angle
Question 19.
Total internal reflection will occur when ray of light travels from …………… medium to …………….. medium.
Answer
Answer: Denser, rarer
Question 20.
Due to refraction, the depth of an optically denser medium appears to be ……………. than its real depth.
Answer
Answer: Less
Question 21.
Due to refraction of light the sun is seen …………….. minutes before actual sunrise.
Answer
Answer: Two
Question 22.
A diamond sparkles due to ……………… of light.
Answer
Answer: Total internal reflection
Question 23.
A ray of light undergoes …………….. twice on passing through a prism.
Answer
Answer: Refraction
Question 24.
One dioptre is …………….. of a lens of focal length ……………… metre.
Answer
Answer: Power, 1 m
Question 25.
The deviation through a prism is minimum when angle of incidence is equal to angle of ……………..
Answer
Answer: Emergence
Question 26.
In the minimum deviation position, the refracted ray in the prism is ………………. to the base of prism.
Answer
Answer: Parallel
Question 27.
In the minimum deviation position of a prism the angle of refraction is equal to ………………. angle of prism.
Answer
Answer: Half
Question 28.
White light consists of …………….. colours.
Answer
Answer: Seven
Question 29.
The magnification for a concave lens is always ………………..
Answer
Answer: positive
Question 30.
A convergent lens made of crown glass (refractive index 1.5) has focal length 20cm in air. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.60, its focal length will be ……………..
Answer
Answer: -160 cm
Question 31.
If two thin lenses of power P1 and P2 are held in contact then the power of the combination will be ……………..
Answer
Answer: P1 + P2
Question 32.
If thin lenses of focal length f1, f2, f3 are in contact, the effective focal length of their combination is ………………
Answer
Answer: \(\frac { 1 }{f}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{f_1}\) + \(\frac { 1 }{f_2}\) + \(\frac { 1 }{f_3}\)
Question 33.
The total magnification m of the combination of three lenses of magnification m1, m2 and m3 is ………………..
Answer
Answer: m1 × m2 × m3
Question 34.
The magnifying power of a simple microscope is ………………. if f is small.
Answer
Answer: Large
Question 35.
In Cassegrainian telescope, a large aperture …………………. mirror & a small aperture ……………… mirror is used.
Answer
Answer: Concave, convex
This NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments with Answers Pdf free download has been put together to help students understand the CBSE Class 12 Physics Ray Optics and Optical Instruments MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers. Hope you found this helpful!