Do you need some help in preparing for your upcoming Class 11 Biology exam? We’ve compiled a list of MCQ questions on Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers to get you started with the subject. Practice NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants with Answers Pdf free download, and learn how smart students prepare well ahead MCQ Questions for Class 11 Biology with Answers.
Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers
Solving Morphology of Flowering Plants Multiple Choice Questions of Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 MCQ can be really beneficial because you will be familiar with all of the topics. These MCQ Questions on Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 with answers provide for a quick review of the Chapter, allowing you to have a better understanding of the subject.
I. Select the correct answer from the following questions:
Question 1.
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of root?
(a) Absence of buds
(b) Presence of chlorophyll
(c) Presence of root cap
(d) Presence of Unicellular hair
Answer
Answer: (b) Presence of chlorophyll
Question 2.
Roots that grow from any part of the plant body other than the radicle are called
(a) Tap roots
(b) Adventitious roots
(c) Modified roots
(d) Aerial roots
Answer
Answer: (b) Adventitious roots.
Question 3.
The place on stem or branch form where one or more leaves arise is called
(a) Apex
(b) Bud
(c) Internode
(d) Node
Answer
Answer: (d) Node
Question 4.
Which one of the following underground, fleshy structure is a stem?
(a) Carrot
(b) Potato
(c) Turnip
(d) Sweet Potato
Answer
Answer: (b) Potato
Question 5.
Phyllode is a modification of
(a) Root
(b) Flower
(c) Petiole
(d) Bud
Answer
Answer: (c) Petiole
Question 6.
Potato tubers are formed at the tips of
(a) Primary roots
(b) Adventitious roots
(c) Petiole
(d) Stolons
Answer
Answer: (d) Stolons
Question 7.
Mesocarp and endocarp is the edible part of the fruit of
(a) Apple
(b) Mango
(c) Banana
(d) Litchi
Answer
Answer: (c) Banana
Question 8.
Drupe is recognised by
(a) Stomy mesocarp
(b) Fleshy seed coat
(c) Thin seed coat
(d) Stony endocarp
Answer
Answer: (d) Stony endocarp
Question 9.
What do you eat in coconut?
(a) Mesocarp
(b) Fruit wall
(c) Entire seed
(d) Embryo
Answer
Answer: (c) Entire seed
Question 10.
The positions of shoot apex in monocot embryo is
(a) Lateral
(b) Basal
(c) Sub-terminal
(d) Terminal
Answer
Answer: (a) Lateral
Question 11.
In which one of the following plants the oil is stored in endosperm
(a) Coconut
(b) Ground nut
(c) Seasame
(d) Soyabean
Answer
Answer: (a) Coconut
Question 12.
In maize, the flower are
(a) Bisexual
(b) Unisexual but on the same plant
(c) Absent
(d) Unisexual but on different plants
Answer
Answer: (b) Unisexual but on the same plant
Question 13.
Epipetalous is condition of
(a) Aestivation of petal
(b) Placentation
(c) Stamens
(d) Position of ovary
Answer
Answer: (c) Stamens
Question 14.
A characteristic of angiosperm is
(a) Flower
(b) Root
(c) Seed
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 15.
An aspect of flower shown in floral formula but not in floral diagram is
(a) Aestivation
(b) Floral symmestry
(c) Position of ovary
(d) Cohesion of floral parts
Answer
Answer: (c) Position of ovary
Question 16.
In grass and banyan tree these are roots arising from parts of the plant other than the radicle, these are called
(a) Adventitious roots
(b) Fibrous root system
(c) Tap root system
(d) Tertiary root system
Answer
Answer: (a) Adventitious roots
Question 17.
In some leguminous plants the leaf base may become swollen, which is called the
(a) Pulvinus
(b) Lamina
(c) Petiole
(d) Leaf base
Answer
Answer: (a) Pulvinus
Question 18.
The arrangement of flowers on the floral axis is termed as
(a) Inflorescence
(b) racemose
(c) cymose
(d) thalamus
Answer
Answer: (a) Inflorescence.
Question 19.
When the floral appendages are in multiple of 3,4 or 5 respec¬tively, a flower may be
(a) Trimerous
(b) Teramerous
(c) Pentamerous
(d) All of these types
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these types
Question 20.
A sterile stamen is called
(a) Staminode
(b) Stigma
(c) Apocarpous
(d) Syncarpous
Answer
Answer: (a) Staminode
II. Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
Solanaceae is a large family, commonly called as the ‘…………’
Answer
Answer: Potato family
Question 2.
Fabaceae family was earlier called ……………, a sub family of family …………….
Answer
Answer: Papilonoideae, Leguminosae
Question 3.
The following floral formula represents the …………… (Family: Brassicaceae)
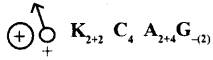
Answer
Answer: mustard plant
Question 4.
In the floral formula, ‘K’ for …………. ‘P’ for ………….. ‘A’ for ……………
Answer
Answer: calyx, perianth, androecium
Question 5.
The outer covering of endosperm separates the embryo by a layer called …………..
Answer
Answer: aleurone layer
Question 6.
The embryo consists of one large and shield shaped cotyledon known as …………. and a short axis with a …………… and a radicle
Answer
Answer: scutellum, Plumule
Question 7.
Above the hilum, is a small pore called the …………..
Answer
Answer: Micropyle
Question 8.
If a fruit is formed without fertilisation of the ovary, it ……………
Answer
Answer: Parthenocarpic fruit.
Question 9.
The calyx is the outer most whorl of the flower and members are called ……………
Answer
Answer: Sepals
Question 10.
If gynoecium is situated in the centre and other parts of the flower are located on the rim of the thalamus almost at the same level, it is called ……………
Answer
Answer: Perigynous
Question 11.
Flowers with bracts, reduced, leaf found in flower are called …………. and those without bracts, ……………
Answer
Answer: bracteate, ebracteate.
Question 12.
In symmetry, the flower may be ……………. or ……………
Answer
Answer: actinomorphic (regular), zymomorphic (bilateral)
Question 13.
A flower having only stamens or carpel is ………….
Answer
Answer: unisexual
Question 14.
………….. is the pattern of arrangement of leaves on the stem or branch.
Answer
Answer: Phvllotaxy
Question 15.
When the incisions of the lamina reach up to the midrib breaking it into a number of leaflets, the leaf is called ………….
Answer
Answer: compound
III. Mark the statements True (T) or False (F):
Question 1.
The study of external features of plants is known as external morpholgy and that of internal features as anatomy.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 2.
The knowledge of external morpholgy of flowering plants is not essential for the study of all branches of botany.
Answer
Answer: False
Question 3.
The root is covered at the apex by a thimble-like structure called the not cap
Answer
Answer: True
Question 4.
A few millimetre above the root cap is the region of meristematic activity.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 5.
Tap roots of carrot, turnip and adventitious roots of sweet potato, get swollen and store food.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 6.
The main function of the stem is spreading out branches bearing leaves, flowers and fruits. It conducts water, minerals and photosynthates.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 7.
Underground stems of potato, ginger, turmeric, zaminkand modify to store food in them.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 8.
A typical leaf consists of three main parts: Leaf base, petiole and lamina.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 9.
In some leguminous plants the leafbase may become swollen, which is called the pulvinus.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 10.
The lamina or the leaf blade is the green expanded part of the leaf with veins and veinlets.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 11.
Veins provide rigidity to the leaf blade and act as channels of transport for water, minerals and food materials.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 12.
Leaves are often modified to perform functions other than photosynthesis. They are converted into tendrils for climbing as in peas, or into spines for defence as in cacti.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 13.
Calyx and corolla are accessory organs, while androecium and gynoecium are reproductive organs.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 14.
When a flower has both androecium and gynoecium, it is termed as bisexual.
Answer
Answer: True
Question 15.
A flower is asymmetric or irregular, if it cannot be divided into similar halves by any vertical plane passing through the centre as in canna.
Answer
Answer: True
IV. Match the items of Column I

Answer
Answer:
(a) → 4
(b) → 15
(c) →13
(d) → 14
(e) → 1
(f) → 3
(g) → 2
(h) → 5
(i) → 6
(j) → 7
(k) → 8
(l) → 9
(m) → 10
(n) → 11
(o) → 12
We hope you found this CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology of Flowering Plants MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers helpful. If you have any questions about NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants with Answers Pdf free download, please share them in the comment box below and we will get back to you at the earliest possible time.